Fire Protection
Scroll down for links with more details on :
– Detection and Communication System
– Fire Hydrant system
– Sprinkler System
– Portable Fire Extinguisher
– Fire Escape
Fire protection systems are standardised elements as approved by the local fire department. For a performance oriented design of fire protection system, various recognised guidelines such as the Singapore Fire Safety Engineering Guidelines [6] can be consulted. The fire authority is notified in advance of any shutdown due to maintenance, especially when the automatic sprinklers are under maintenance. Such shutdowns could be scheduled during normal working hours and finished in the shortest possible time. If required, special precautions (e.g. fire petrol, temporary water connection, etc.) could be employed [7]. The fire safety defects raised in this chapter concern (a) detection and communication system; (b) Fire hydrant systems; (c) Fire Hose; (d) Sprinkler system; (e) Portable fire extinguisher (e.g. poor discharge of portable fire extinguisher and obstructed fire door); (f) Fire escape and related services . Considerations for the maintainability of fire protection systems at the design stage could prevent the occurrence of these identified defects. Making sure that the fire protection system is in proper condition could help avoid inconveniences during cases of false alarms.
Fire Protection System
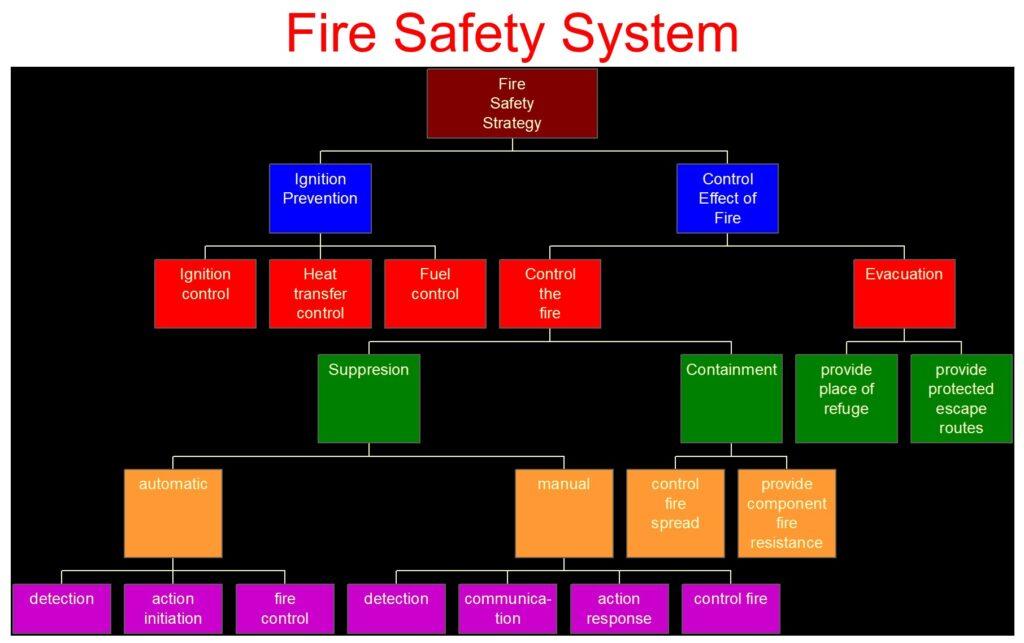
The two main objectives of a fire protection system are: (a) to reduce the risk of losing lives to the minimum, and (b) the protection of the building and its contents, as well as to prevent/minimise the spreading of the fire to adjacent buildings. It does so by:
- preventing the initiation of fire
- restricting the growth and spread of fire
- containing the fire within specified boundaries through compartmentation
- providing some means of escape for the occupants
- controlling the fire using automatic devices and by active fire-fighting.
A safe building begins with a carefully analysed architectural layout and planned maintenance schedules. This includes the appropriate locations and construction of the various subsystems and regular maintenance and repairs.
Most designs and operations of fire protection systems are strictly governed by local fire safety codes, as well as local and international standards. The designers and facilities managers (FM) need to be conscious of these codes and standards during the design and post-occupancy phases.
Reference is made to:
- SCDF Fire Code — Code of practice for fire precaution in buildings
- NFPA 1 — Fire Code
- SS 645 — Code of practice for the installation and servicing of electrical fire alarm systems
- SS 575 — Code of practice for the fire hydrant, rising mains and hose reel system
- CP 52 — Code of practice for automatic fire sprinkler system
Maintainability of Fire Protection System
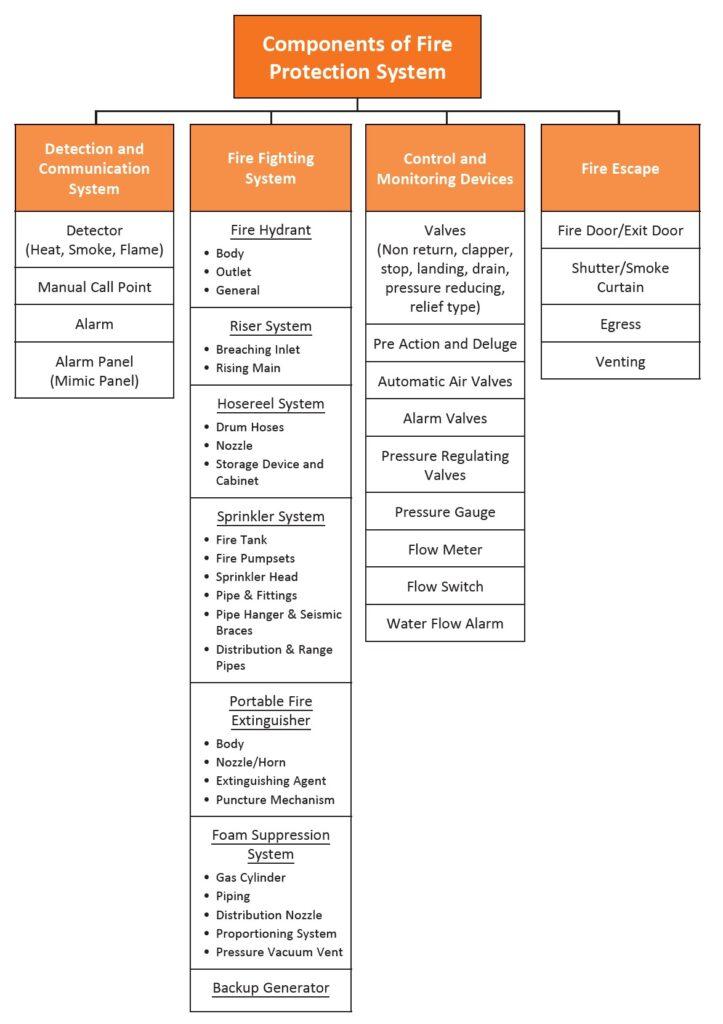
A fire protection system can be subdivided into four major components, namely, (1) a detection and communication system, (2) a fire fighting system, (3) control and monitoring devices, and (4) fire escape. Each component can be further structured and divided into major sub components which are commonly found in commercial buildings.
The main tests for fire protection systems are:
- Fire Alarm System Test
- Hydrostatic Test
- Dry Riser Test
- Wet Riser Test
- Hose Reel Test
Common Defects
Fire protection engineering is multi-disciplinary. Planning the layout and escape routes involves the expertise of architecture, while the fire rating of the construction is covered by civil engineering. Mechanical engineering’s coverage involves calculating the flow of water through the pipe work, the discharge of the extinguishing agent through equipment nozzles, and fluid mechanics. Finally, chemical engineering deals with the hazards of chemical interaction and processes.
The common defects often faced by maintenance teams are summarised in the figure below. Many of these common defects could be avoided if maintainability is considered right from the design stage. Many cases are related to (1) exits not properly marked or blocked or locked, (2) the lack of/an inoperative alarm system, (3) missing fire hose(s), standpipe(s) or extinguishers, (4) the absence of a sprinkler system or a sprinkler system’s failure to respond, and (5) no fire training provided to the occupants or maintenance team.
Common problems associated with fire protection in a facility include:


Detection and Communication System




Fire Escape and Related Services
For more information on Fire Protection, see the PDF below:
Code of Practice for Fire Precautions in Buildings
Standards
SINGAPORE STANDARDS
SS 638 CoP for Wiring of Electrical Equipment of Buildings
SS 645 CoP for Installation and Servicing of Electrical Fire Alarm System
SS CP 52 CoP for Automatic Fire Sprinkler System
SS 99 Specifications for Welded Low Carbon Steel Cylinders for Storage and Transportation of Low-Pressure Liquefiable Gases
SS 213 Unplasticised PVC Pipes and Fittings for Soil, Waste and Vent Application
SS EN 3-10 Portable Fire Extinguishers
SS 233 Specifications for Flexible Rubber Tubing, Rubber Hose and Rubber Hose Assemblies for Use in LPG Vapour Phase Installations
IEC 60079 Electrical Apparatus for Explosive Gas Atmospheres
SS IEC 60598-2-22 Luminaires – Particular Requirements for Luminaires for Emergency Lighting
SS 281 Specifications for Pressure Regulators for LPG
SS 586 Caution Labelling for Hazardous Substances
SS 294 Specifications for Valves for Use with Domestic and Industrial LPG Cylinders
SS 299 Fire Resistant Cables
SS 332 Specification for Fire Door
SS 333 Specification for Fire Dampers
SS 489 Specification for Fire Shutters
SS 508 Graphical Symbols – Safety Colours & Safety Signs
Pt 1 Design Principles for Safety Signs & Safety Markings
Pt 2 Design Principles for Product Safety Labels
SS 532 CoP for the Storage of Flammable Liquids
SS 535 CoP for Installation, Operation, Maintenance, Performance and Constructional Requirements of Mains Failure Standby Generating Systems
SS 546 CoP for Emergency Voice Communication Systems in Buildings
SS 550 CoP for Installation, Operation and Maintenance of El Passenger and Goods Lifts
SS 551 CoP for Earthing
SS 563 CoP for the Design, Installation & Maintenance of Emergency Lighting and Power Supply Systems in Building Formerly CP 19
Pt 1 Emergency lighting
Pt 2 Installation Requirements and Maintenance Procedures
SS 572 CoP for the Use of Timber in Buildings
SS 575 CoP for Fire Hydrant, Rising Mains and Hose Reel Systems
SS 578 CoP for Use and Maintenance of Portable Fire Extinguishers
SS 586 Specification for Hazard Communication for Hazardous Chemicals and Dangerous Goods
SS 608 CoP for Gas Installation
SS 634 Plant Processing Facilities in Oil, Chemical and Process Industries
SS EN 3-7 Portable Fire Extinguishers – Part 7 : Characteristics, performance requirements and test methods
SS EN 3-8 Portable Fire Extinguishers – Part 8 : Additional requirements to SS EN 3-7 for the construction, resistance to pressure and mechanical tests for extinguishers with a maximum allowable pressure equal to or lower than 30 bar
SS EN 3-9 Portable Fire Extinguishers – Part 9 : Additional requirements to SS EN 3-7 for pressure resistance if CO extinguishers
SS EN 3-10 Portable Fire Extinguishers – Part 10 : Provisions for evaluating the conformity of a portable fire extinguisher to SS EN 3-7
AMERICAN STANDARDS
ASTM D635 Standard Test Method for Rate of Burning and/or Extent &Time of Burning of Plastics in a Horizontal Position
ASTM E108 Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Roof Coverings
ASTM E119 Standard Test Methods for Fire Tests of Building Construction & Materials
NFPA 16 Standard for the Installation of Foam-Water Sprinkler and Foam-Water Spray Systems Formerly NFPA 16A
NFPA 30 Flammable & Combustible Liquids Code
NFPA 33 Standard for Spray Application Using Flammable or Combustible Materials
NFPA 45 Standard on Fire Protection for Laboratories Using Chemicals
NFPA 54 National Fuel Gas Code
NFPA 55 Compressed Gases and Cryogenic Fluids Code
NFPA 58 Liquefied Petroleum Gas Code
NFPA 251 Standard Methods of Tests of Fire Resistance of Building Construction & Materials
NFPA 262 Standard Methods of Tests for Flame Travel and Smoke of Wires and Cables for Use in Air-Handling Spaces
NFPA 400 Hazardous Materials Code
NFPA 432 Code for the Storage of Organic Peroxide Formulations
NFPA 495 Explosive Materials Code
NFPA 502 Standard for Road Tunnels, Bridges and other Limited Access Highways
NFPA 750 Standard on Water Mist Fire Protection Systems
UL 132 Standard for Safety Relief Valves for Anhydrous Ammonia and LP-Gas
UL 144 Standard for LP-Gas Regulators
UL 300 Standard for Fire Testing of Fire Extinguishing Systems for Protection of Commercial Cooking Equipment
AUSTRALIAN STANDARDS
AS 1530 Methods for Fire Tests on Building Materials, Components & Structures Pt 4 Fire-resistance Test of Elements of Construction
AS 2208 Safety Glazing Materials in Buildings
AS 2714 The Storage & Handling of Organic Peroxides
AS 2941 Fixed Fire Protection Installations – Pumpset Systems
AS 4391 Smoke Management Systems – Hot Smoke Test
AS 4326 The Storage & Handling of Oxidizing Agents
AS 4587 Water Mist Fire Protection Systems – System Design, Installation and Commissioning
BRITISH STANDARDS
BR 186 Design Principles for Smoke Ventilation in Enclosed Shopping Centres,
BR 258 Design Approaches for Smoke Control in Atrium Buildings
BR 368 Design Methodologies for Smoke and Heat Exhaust Ventilation
BS 476 Fire Tests on Building Materials and Structures
Pt 4 Non-Combustibility Test for Materials
Pt 5 Method of Test for Ignitability
Pt 6 Method of Test for Fire Propagation for Products
Pt 7 Method of Test to Determine the Classification of the Surface Spread of Flame of Products
Pt 11 Method for Assessing the Heat Emission from Building Materials
Pt 20 Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Elements of Construction (General Principles)
Pt 21 Methods for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Load- Bearing Elements of Construction
Pt 22 Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Non-Load- Bearing Elements of Construction
Pt 23 Methods for Determination of the Contribution of Components to the Fire Resistance of a Structure
Pt 24 Method for Determination of the Fire Resistance of Ventilation Ducts
BS EN 520 Pt 1 Specification for Plasterboard Excluding Materials Submitted to Secondary Operations
BS 4514 Specification for Unplasticized PVC Soil and Ventilating Pipes of 82.4mm Minimum Mean Outside Diameter, and Fittings and Accessories of 82.4mm and of Other Sizes
BS 5041 Fire Hydrant Systems Equipment
Pt 1 Specification for Landing Valves for Wet Risers
Pt 3 Specification for Inlet Breechings for Dry Riser Inlets
BS 5234 Partitions (including matching linings)
Pt 2 Specification for Performance Requirements for Strength and Robustness including Methods of Test
BS 5852 Methods of Test for Assessment of the Ignitability of Upholstered Seating by Smouldering and Flaming Ignition Source
BS 6206 Specification for Impact Performance Requirements for Flat Safety Glass and Safety Plastics for Use in Buildings
BS 6391 Specification for Non-Percolating Layflat Delivery Hoses and Hose Assemblies for Fire Fighting Purposes
BS 7346 Components for Smoke and Heat Control Systems, Pt 7 CoP on Functional Recommendations and Calculation Methods for Smoke and Heat Control Systems for Covered Car Parks
BS 8202 Coatings for Fire Protection of Building Elements, Pt 2 CoP for the Use of Intumescent Coating Systems to Metallic Substrates for Providing Fire Resistance
BS EN 54 Fire Detection and Alarm Systems, Pt 2 Control and Indicating Equipment, Pt 4 Power Supply Equipment
BS EN 520 Gypsum Plasterboards. Definitions, Requirements and Test Methods
BS EN 12101-1 Smoke & Heat Control Systems – Specification for Smoke Barriers
BS EN 12101-3 Smoke & Heat Control Systems – Specification for Powered Smoke & Heat Control Ventilators (Fans) Replaces BS 7346 Pt 2
BS EN 13501-1 Fire Test to Building Materials – Classification
BS EN 50054 Electrical Apparatus for the Detection and Measurement of Combustible Gases. – General Requirements and Test Methods
BS EN 50057 Electrical Apparatus for the Detection and Measurement of Combustible Gases. – Performance Requirements for Group II Apparatus Indicating up to 100% Lower Explosive Limit
BS EN 60079-14 Explosive Atmosphere. Electrical Installations Design, Selection and Erection Replaces BS 5345 Pt 1 & 3
BS EN IEC 62485-2 Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations. – Stationary Batteries
BS EN IEC 62485-3 Safety Requirements for Secondary Batteries and Battery Installations. – Traction Batteries
EUROPEAN STANDARDS
EN 81 – 58 Safety Rules for the Construction and Installation of Lifts. Examination and Tests. Part 58 – Landing Doors Fire Resistance Test
EN 671 – 1 Fixed Firefighting Systems. Hose Systems. Hose Reels with Semi-Rigid Hose
EN 13823 Reaction to Fire Tests for Building Products – Building Products excluding Floorings exposed to the Thermal Attack by a Single Burning Item
EN ISO 1182 Reaction to Fire Tests for Products – Non-Combustibility Test
EN ISO 1716 Reaction to Fire Tests for Building Products – Determination of the Gross Heat of Combustion (Calorific Value)
EN ISO 11925 -2 Reaction to Fire Tests – Ignitability of Products subjected to Direct Impingement of Flame – Part 2 : Single Flame Source Test
IEC STANDARDS
IEC 60079 Explosive Atmospheres
ISO STANDARDS
ISO 834 Fire resistance Tests – Elements of Building Construction
ISO 1896 Thermal Insulating Asbestos Boards
ISO 5149 Refrigerating Systems and Heat Pumps – Safety and Environment Requirements