Case 1
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Avoid water infiltration into the structure by keeping the concrete slab as dry as possible, using good housekeeping practices. Provide protective measures to prevent waterproofing membrane from damage by any activities on site in accordance with SS 637 or equivalent. Carry out regular inspection for signs of water seepage using NDT diagnostic techniques. Monthly cleaning and timely repair should be carried out in accordance with SS 637 or equivalent. Remediate any leakage by removal of screed, clearing all loose particles and re-application of waterproofing. Localised porous concrete can be repaired by polyurethane (PU) grouting by injecting into either the passive or active side of the slab/wall. Repair leakage at cracks by injecting PU grout, or the Flood Infusion Method.
Regular inspections should be carried out of wet areas, especially at vulnerable interfaces/joints between
different materials. Use non-destructive testing (NDT) in this regard. Water leakage can be identified using thermography images in accordance with BS ISO 10880 or by using a moisture meter. Repair work can be done using polyurethane (PU) grouting/injection for local seepages. For more severe incidents, laying of new waterproof screed is strongly recommended.
Diagnostics of Defect (see also NDT)
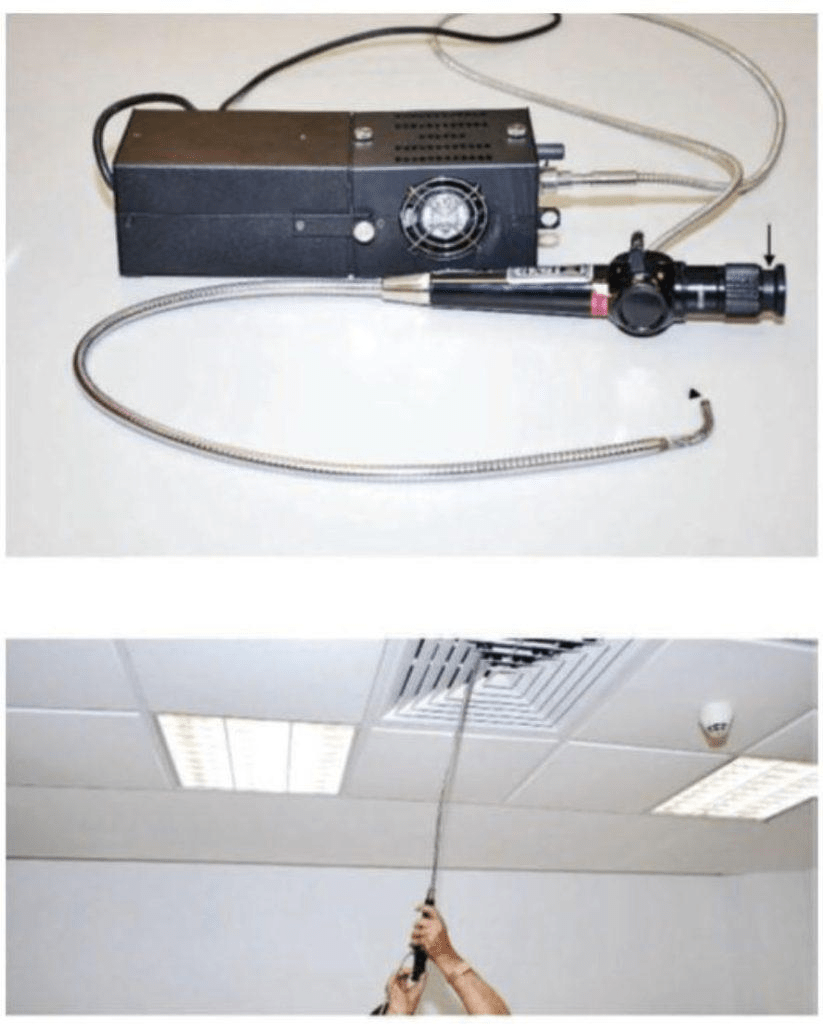
This instrument is useful when services are concealed. There have been many cases of collapse of large area of false ceiling, due to weight of accumulation of water or condensate. Regular inspection using a fibrescope/borescope could prevent such accidents.
A fibrescope or a flexible borescope is a flexible optical inspection device that consists of fibre optic bundles with an eyepiece at one end and a lens at the other.
A fibrescope usually comes in two bundles: (i) a fibre optic light bundle that is for illuminating the object to be investigated, and (ii) a fibre optic image bundle to relay the image to the eyepiece. It allows a direct visual inspection for an otherwise inaccessible part, as observations of remote, difficult-to-reach areas can be made through a video monitor with high-resolution images. The flexible fibres allow it to be manoevred in hard-to-reach or inaccessible areas.
It is often used to verify findings from other tests, such as infrared thermography or impact-echo testing.
Common applications include:
– Inspection of connecting condition behind the external cladding wall of a building.
– Inspection of defects on concrete surface(s) in a deep and narrow gap.
– Determination of corrosion condition of steel tendon(s) inside post-tensioning ducts of pre-stressed structural member(s).
– Investigation of service pipes, ducts and other inaccessible areas.
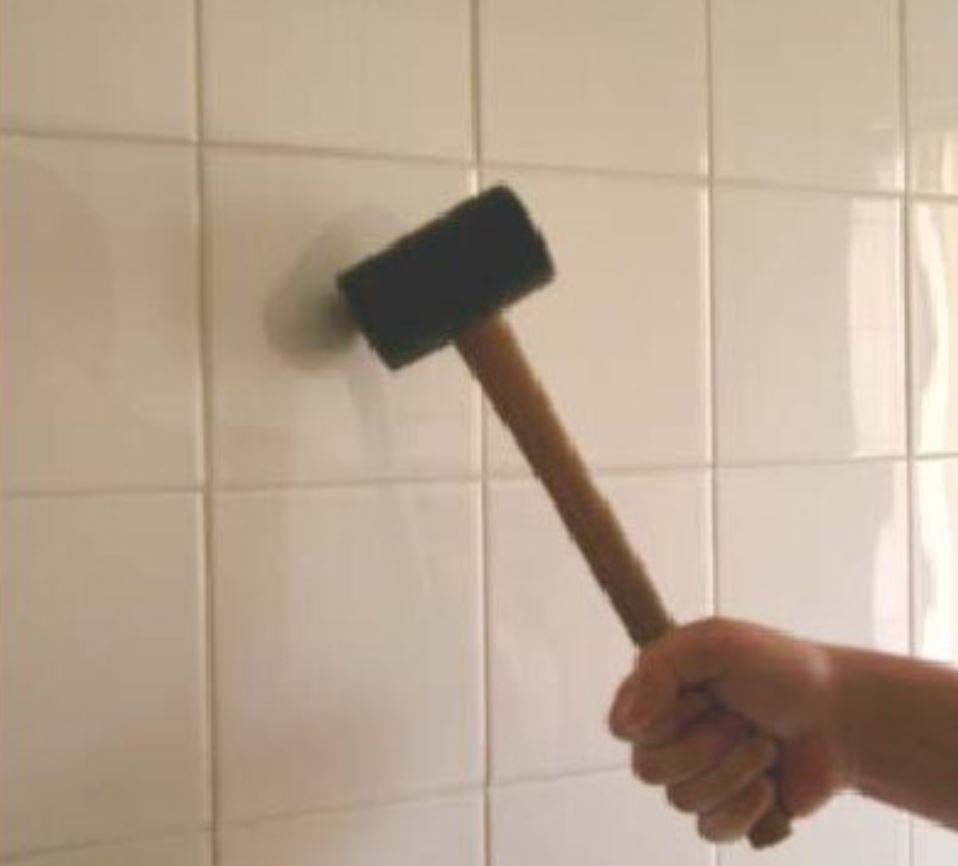
Hammer Tapping Test
Tapping test may be used to detect hollowness, delamination, spalled or debonded plaster.by listening to the ‘void’ sound.
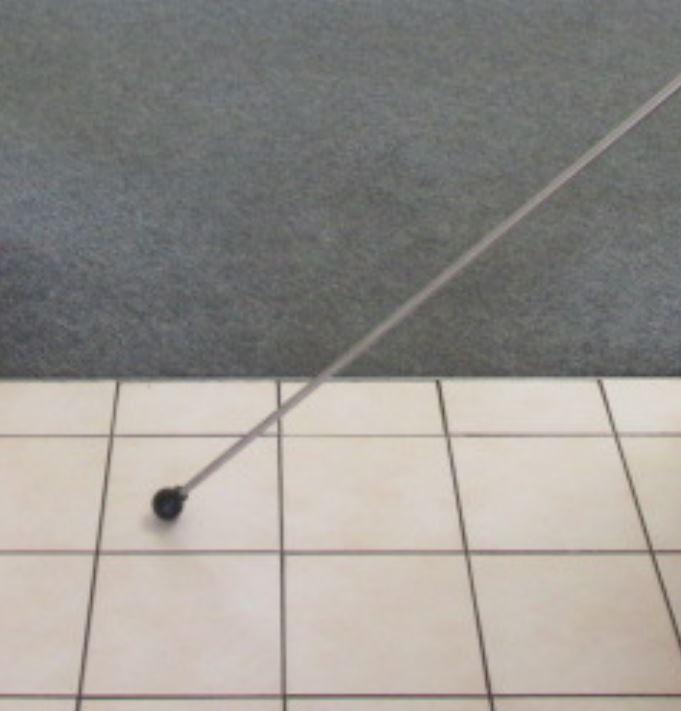




Protimeter / Moisture Meter
Moisture meter is used to determine the presence of moisture. Moisture readings can be taken within masonry walls, dry walls, insulation, concrete members, roofing, wood construction, and other building components.
