Vertical Greenery
Maintenance and Diagnostics
The selection and maintenance of vertical greenery system is crucial towards the success and survival rate of the vertical greenery system. Important factors to consider during the maintenance of the vertical greenery system include choice of plant; type of irrigation system used and sun orientation. Failure to choose the correct vertical greenery system and apply its respective proper maintenance procedures would make the vertical greenery system obsolete42. Vertical greenery technology is still at its infancy stage due to the lack of expertise pertaining to the maintenance of vertical greenery24. However, proper plant choice and a well-planned schedule for maintenance would increase the success rate of the vertical greenery system while keeping the maintenance cost low. In making a decision when looking into the maintenance procedures to keep these vertical greenery system healthy and functioning properly, a clear understanding on how each vertical greenery system works need to be established.
There are four (4) most commonly utilized variants of vertical greenery system currently available in the market:
- Modular panel system
- Consists of 3 key components – structural frame, panels, and growth medium with plants and irrigation system
- The automated irrigation system maybe complicated to install and maintain as dirt may clogged up the water drips and there are chances where sensors may malfunction
- Maintenance cost of the system would be rather high as there will be the need to rent heavy equipment such as scissor lifts to allow the maintenance team to reach the higher part of the panel structure
- Direct connection system
- Vegetation is planted in 0.5m free strip along the façade of the building
- Vegetation alone are capable of climbing the wall without any other support other than the façade of the building
- Vegetation will damage the façade of the building as its tendrils clinched on the surface of the façade
- The plants are free to grow in any direction. Thereby making it difficult for the maintenance team to trim the plants if they were to overgrow
- Cable or wired structural support system
- There will be a little distance between the structure and the façade of the building allowing a layer of gap in-between
- A planter box will be located below the trellis structure to allow the plants to grow from the planter and onto the structural systems
- Synthetic Felt System
- Individual pockets of space manufactured with synthetic felt mounted to plastic panels where individual plant will be placed at
- Irrigation system will be similar to the modular panel system where individual irrigation pipe line will be supplied to individual pocket of plants to ensure even and timely irrigation
- Maintenance is both labor intensive and costly
Factors affecting VGS maintenance
As a vertical greenery system is a collective living organism, it had to be looked after and be maintained39. The maintenance needs and costs would depend on the greening system type15, as well as different type of vertical greenery system requires different amount and type of maintenance method. Vertical greenery components and systems require careful protection and maintenance once they are installed as they are crucial to the long-term health and sustainability of the vertical greenery system43. Below are some of the factors to be considered in maintainability of vertical greenery systems:
Client Expectation
It is important that maintenance requirements are fully discussed with the owner during the planning and design stage44. Client expectation plays a critical role in ensuring the success of the vertical greenery. The early involvement of various professionals is essential to ensure smoother coordination and prevent conflicts from arising among them. For instance, the planning for the inclusion of external vertical greenery in a project at the initial design stages provides greater flexibility for the design of the façade, structural supports and mechanical watering system, and thus reduces the cost of implementation45. Moreover, the contractor needs to understand the client expectation for the vertical greenery wall to enable them to think if the intended wall is feasible to install and the level of maintenance it requires. Thus, the client must understand and be willing to commit to the maintenance needs, labour and resources required, as well as the overall costs of maintenance prior to final design and construction7.
Accessibility
Accessibility plays a vital role in the maintenance process of the VGS. When efficient access are not provided, this in turn increases the maintenance cost, due to the need of hiring special access systems or due to the escalating number of defects created by no access for the maintenance activities and also no maintenance at all24. Access point should be provided in order to access to the wall for maintenance. For low vertical greenery wall can be accessed by ladder for walls only a few yards high, but for those from 10 – 30m high, a vehicle-mounted cradle is necessary39. On the other hand, for very high walls or where access is difficult, maintenance is carried out from the top by roping down a mobile platform, like window-cleaners working on high buildings39. For vertical greenery system, which cannot be easily accessed from within the building, they will have to use a special equipment or methods such as the utilization of scissor lift to reach the top part of the green wall structure that could often spam up to a few stories in height. For efficiency, green wall should not be placed in a space where it will be difficult or costly to access on a regular basis. Proper lifts and equipment needed should be accessible at all times for easy maintenance and repair work to be carried out. Workers need to work in spacious area that allow for reasonably comfortable positions and equipment.
Site location
Environmental factors have a great influence on the plant species selection where it directly affects the well-being and sustainability of the vertical greenery. This is because different plant species require differing amount of sunlight, wind and moisture46. Site analysis should be carried out to have a better understanding on the existing site condition and to narrow out the best vertical greenery system that would be the most ideal for the existing site. An in-depth analysis would usually include the sun path analysis, wind velocity and existing drainage system. Other environmental factors to consider are light requirement and wind effect47; as follows:
- Light requirement – the site surrounding will affect the amount of sunlight received by the plants7. Generally, plants located on west-facing walls will experience higher levels of temperature fluctuation due to the direct exposure of solar radiation48. Hence, the orientation of the walls where the vertical greenery systems are placed should be taken into account as well. Moreover, plants grown at the top of the wall will receive different amount of light as compared to those at the bottom of the wall18. Therefore, it is important to understand the lighting condition of the site before selecting the appropriate plants7.
- Wind Effect – affects the selection of plants, since wind around buildings is a very variable phenomenon18. Strong winds because quick drying and this will cause plants to become unhealthy and water-stressed7. Hence, it is essential to understand the wind effect of location of the vertical greenery wall before making the right choice in the plants selection.
Planting Media
Soil plays a part in providing support and nutrients for the plants. However, due to the weight load of soil, the soils are replaced with lightweight planting media such as perlite, vermiculite, peat moss, etc. The mixture of the planting mix has to allow water retention and infiltration to prolong the life of the vertical greenery. Besides the issue on the soil weight, the fact that soil erode is another reason contractors are seeking alternative planting media. Thus, it is necessary to choose the appropriate planting media in order for the vertical greenery to sustain and if possible, minimize the level of maintenance.
Irrigation Systems
Irrigation is the lifeline of any vertical greenery system7. As vertical greenery walls are hydroponic systems where water and nutrients are fed via mechanical irrigation, it is important to establish control and timing of the watering system45. Drip irrigation is the most commonly used irrigation method for vertical greenery system as it is known as the most water efficient method of irrigation. As water drops right near the root zone of a plant in a dripping motion, it can steadily minimize water wastage that might be loss through evaporation and runoff.
Plants selections
Besides adhering to the proper maintenance practices, the choice of the right type of plants in the beginning is important49. For a vertical greenery system to be successful, the selection of plants is very crucial. The criteria for plant selection should be based on the type of systems used, the intended planting concept, environmental factors, budget and expected degree of maintenance7. The selection of plants for vertical greenery will have to depend on several criteria:
- Local climate- chances of survival for plants that are not accustomed to grow in the local climate are much lower. By utilizing native plants, the amount of irrigation needed is reduced, as most of the plants need minimal irrigation beyond normal rainfall. Native plants are also capable of defending themselves against local pest thereby reducing or eliminating the use of pesticides.
- Adaptability and suitability– it is important to take note that survival and growth of certain plant species are dependent on the microclimatic conditions48. The selected plant species must be able to tolerate local high temperature conditions, periodic temperature fluctuation, intensive sunlight and low soil moisture; due to high rate of evaporation39.
- Growth characteristic – certain plant species requires high level of maintenance such as frequent watering, feeding or pruning. These factors add to the amount of time and cost needed to upkeep the vertical greenery to ensure the survival of the plants. Different plant species have different growth rate. Slow growing or blooming plants may affect the initial ‘look’ that the landscape architect had set out to archive with their design. Depending on the project duration, and the effect that the landscape architect is trying to archive, plants will be selected based on their growth rate.
- Desired appearance – depending on what the look that the landscape architect is trying to achieve, plants of different shape, size and colors will be used to achieve the intended design/concept.
- Type of system- each vertical greenery system has its own unique way for the placement of plants. Some system requires the plants to be grown vertically while others require the plant to grow horizontally. For example, plants grown vertically need roots strong enough to hold onto the growth medium.
- Budget –depending on the project’s budget, the type of plants to be included in the plant palette will be decided on their maintenance requirement, hardiness level, growth rate and acquiring cost. These factors will affect the initial purchase cost and in the end, the maintenance and running cost of the vertical greenery.
Plants are living creatures that require moisture and fertilizer for growth, and might be damaged by various diseases. Therefore, regular maintenance is essential to keep the greening good-looking. Maintenance costs can be reduced greatly with an early understanding of the requirements of VGS. The amount of maintenance is very much influenced by expectations of the client or the building’s end users. Thus, maintenance issues should be discussed with the client in the early stages of design to ensure that they can be properly addressed7. Establishing a well-understood maintenance regime with facilities management personnel, especially at the specification stage, will greatly improve the likelihood of survival of the wall45.
Types of maintenance
Maintenance needs and costs depend on the greening system type50. Maintenance of vertical greenery comprises of different activities. They can be divided into irrigation and system check, fertilization, trimming and maintenance of plant, replacement of sick plant, and pest control and fungicide51. Such maintenance is necessary to keep the vertical greenery in good condition in the aspect of aesthetics, hygiene, cleanliness and functionality. The following considerations for the maintainability of the vertical greenery system:
1. Structural component
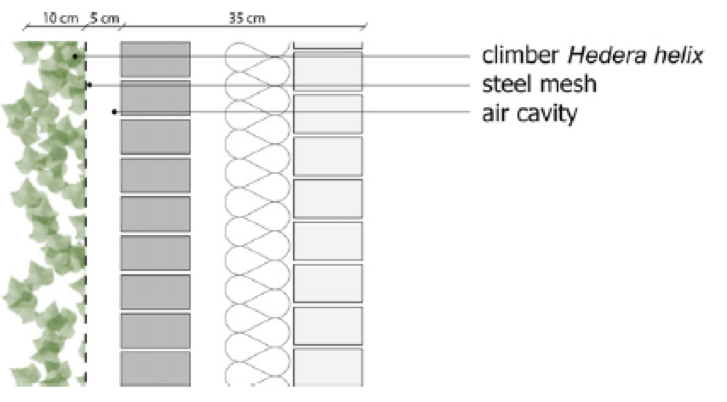
Regular checks are recommended as part of the preventive maintenance measures to identify any small cracks or holes as these openings create opportunities for water to enter. If untreated, corrosion might occur which in long term may result in both the weakening and failure of a steel structure that poses a threat to the safety of the building’s occupants and the surrounding people. In the case of the cable or wired structural support system, regular checks during or in-between maintenance check should be carried out to ensure the overall structural rigidity of the supporting structural frame. The hot and humid weather makes it important to allow for ventilation. Ensure that the vertical greenery system is attached at a distance away from the vertical surface to avoid trapping moisture and prevents deterioration of structure material52 as shown in Figure 8.
During maintenance, conduct frequent checks and measurements on the load-bearing capacity of the support system, taking into account the net weight of the entire system when the vegetation and substrates are fully-saturated. Tabulation of the net weight includes the dead and live loads comprising of the support structure, irrigation system, substrates and plants and possible, weight of maintenance workers as well. Ensure that the load is not beyond the load bearing capability.
2. Irrigation system
Regular checks on the irrigation system are required to ensure the smooth operation of the system, preventing water supply shortages or excess. Irrigation for vertical greenery should be done once or twice a day according to the program set in the controller. Monitoring for frequency and quantity of irrigation is necessary to suit the condition of the plants. Plants can be killed by either ignoring irrigation during periods of extreme drought or more frequently by overwatering53. Materials such as dead leaves, soil and mud must be removed from the drainage system to prevent water collection, which could cause breeding of mosquitoes47. Other maintenance of irrigation can be done simply by:
- Ensuring there is no blockage in the irrigation supply lines with the removal fallen leaves, planting media or any other materials.
- Ensure no clogging due to sediments entering the thin tubing of the drip line thereby causing clogs and emitter malfunctions.
- Ensure water supply points are provided and waterproofing protection treatments are done to the external wall.
- Ensure fittings and pipelines are immediately replaced if found defective to prevent additional cost from water leakage
3. Drainage system
Drainage system is used to collect and direct the excess irrigation or rainfall away from the green wall structure to prevent excessive water flooding of the soil media. If left untreated over a period of time, it will ultimately result in root rot where in severe cases would lead to death of the plant. Regular checks should include the removal of any debris such as dead leafs in the drainage to prevent choking or blocking. The replacement of filter and clearance of the drainage should also be carried out periodically to prevent clogging in the drainage system. Gutters are checked to ensure non-blockage and prevent mosquito breeding. As mosquito breeding in Singapore is a growing concern, frequent checks are necessary when the green wall is put in place49. Some vertical garden systems are especially designed to have a built-in reservoir that stores excess water that plants can tap on. Such systems reduce the reliance of constant irrigation found in systems with such in-built reservoirs53.
4. Fertilization
Fertilization for vertical greenery is important to ensure sufficient nutrients for the plants. It is recommended to be done monthly. The simplest approach is to add sufficient nutrients that is required by the plant into the water and distribute them through the irrigation system54.
5. Removal of weed
Airborne seed germination involving weed seeds and fern spores in the atmosphere needs to be prevented. Once the seed lands on the fertile green wall medium, they will start to grow at a very fast and alarming rate. These unwanted spontaneous weeds should be removed immediately during regular checks before they take hold55.
6. Aesthetic maintenance
Green facades are typically vines and climbing plants grown upwards from the ground on specially designed support along the vertical surface, thereby forming a leafy screen over the surface. However, it has to be noted that climbing plants will coagulate at the top to compete for sunlight; therefore, maintenance regime has to be stringent to ensure uniform green coverage. To maintain lush coverage, ensure plants are in a uniformed spacing arrangement. The maintenance regime involves daily inspection to replace any unsightly strand as can be seen. Pruning works are executed monthly, depending on the planting media, weather conditions and the characteristics of the plants on each system56. Moreover, trimming and maintenance of the plant cannot be taken lightly. It does not only ensure the aesthetics standard of the vertical greenery, it also ensures the safety of the occupants in the building. Trimming of the plants prevents the bigger branches from being pulled out in extreme weather or falling due to their weight. In addition, unsightly plants such as yellow leaves and dead branches are cleared away to ensure an acceptable aesthetic quality. Replacement of plants will only be required when it is dead or sick54.