Case 1
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Maintenance
Flat roofs should be screeded to fall and be periodically inspected for any ponding. Visual observations
of free-flowing water towards the outlets should be made to ensure that the water drains off thoroughly so as to avoid leftover ponding in the gutter or on the reinforced concrete flat roof in accordance with BS
8221-1, SS 509-1 or equivalent.
Free flow in gutters and downspouts should be maintained. They should be kept clear of leaves and
other debris.
Whether flat roof are constructed of concrete or timber, they need to be laid to adequate falls and incorporate a vapour barrier. The generally accepted minimum fall is 1 in 80, but the latest recommendation is 1 in 40 to make allowance for any inaccuracies on the site and possible deflection of the roof structure.
Ponding occur only when there is unevenness of the slab surfaces. Regular inspection should be carried out especially after a downpour. This allow for visual inspection of possible ponding area. When ponding happen, immediate repair is needed. Apply a layer of screed so as to level the surface and take note of the fall, directing the flow of the water to the drainage area.
Diagnostics of Defects (see also NDT)
Thermography
Thermography can be used to identify the position of cracks. A range of crack widths, representing mechanical damage, has been induced under controlled laboratory conditions. The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions.
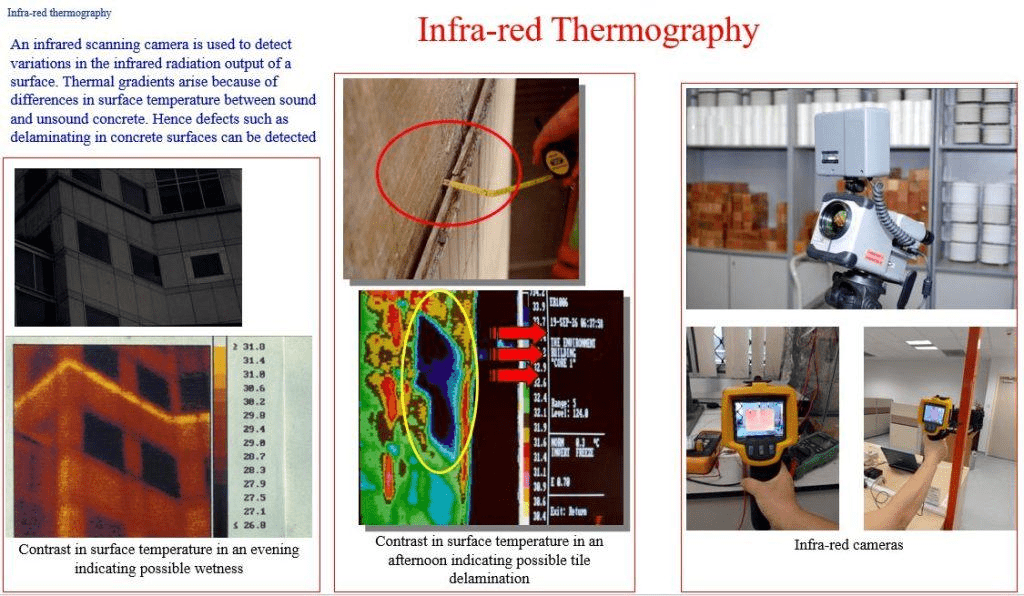
The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions. Thermo tracer is an advanced equipment used in thermograph technology.
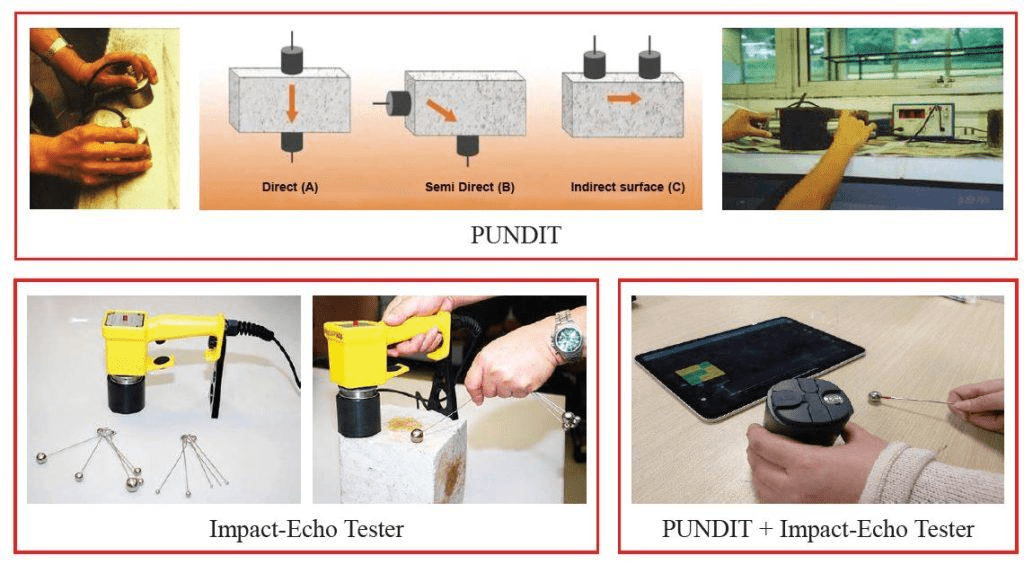
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
UPV can identify non-homogeneous conditions such as voids, cracks and honeycombs using the optional hand-held terminal. This method can also be used to estimate the depth of cracks.
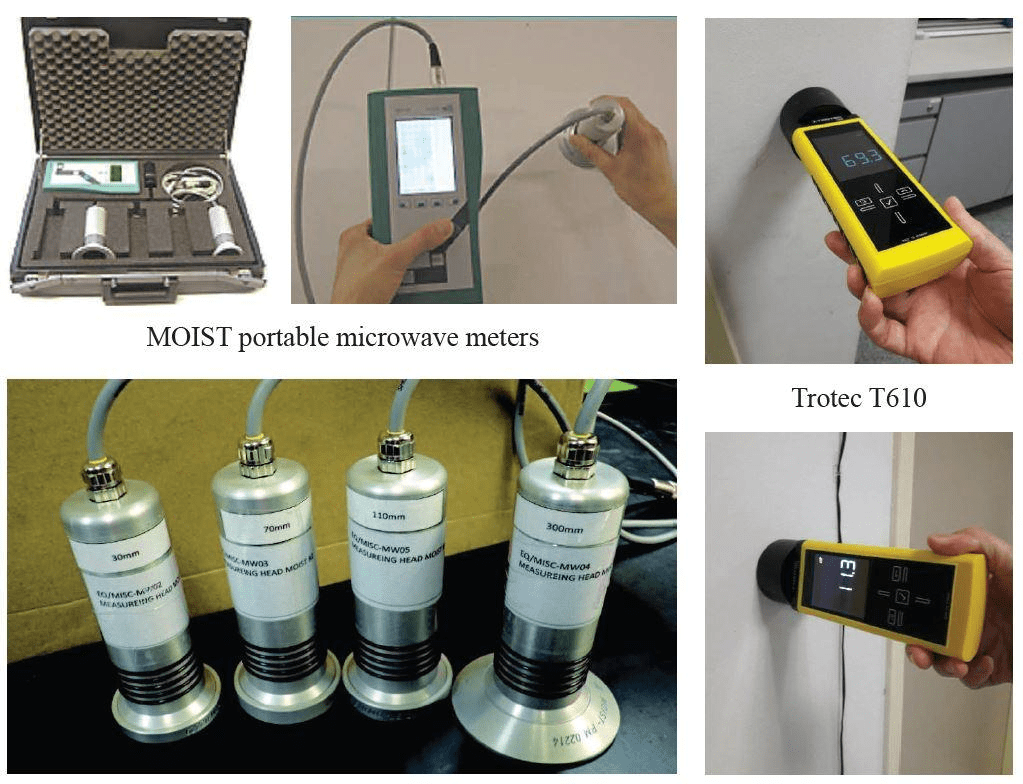
Microwave tomography is a technique to measure the moisture of various materials based on the relatively high dielectric constant of “water” in comparison to the dielectric properties of the material. An electrical field (microwave) is applied to the material, and the microwave induces oscillations of bipolar molecules (i.e., water). Water molecules will reflect and absorb an electrical field during oscillations. A higher electrical field reflected indicates higher water content.
The technique is non-destructive and applicable to wood, brickwork and concrete. The uniqueness of this technique is its ability to measure moisture content at various depths up to 110 mm, allowing the plotting of a 3-D contour of moisture content and facilitating the tracing of the water source.