Case 3
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Regular inspections should be carried out of wet areas, especially at vulnerable interfaces/joints between
different materials. Use non-destructive testing (NDT) in this regard. Water leakage can be identified using thermography images in accordance with BS ISO 10880 or by using a moisture meter. Repair work can be done using polyurethane (PU) grouting/injection for local seepages. For more severe incidents, laying of new waterproof screed is strongly recommended.
- It is known that good quality concrete does not require extensive maintenance. However, due to external factors it might have some defects even without reaching its design life.
- An efficient inspection system should be adopted to ensure the conduct of regular checks such as visual inspections periodically to detect such defects.
- Suitable instruments and techniques should be used to diagnose defects properly. Diagnosis involves a process in which experts investigate the buildings’ conditions, carry out tests, evaluate, make recommendations for remedial actions where necessary and predict the future performance of a building.
Diagnostics of Defect (see also NDT)
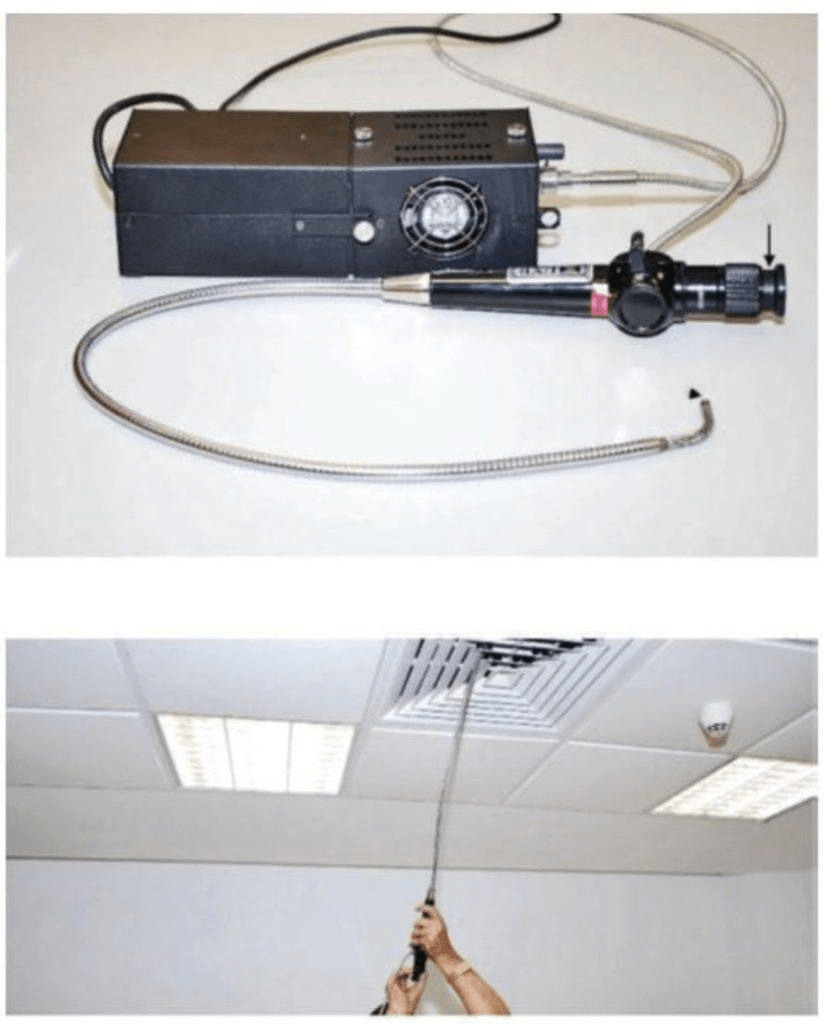
This instrument is useful when services are concealed. There have been many cases of collapse of large area of false ceiling, due to weight of accumulation of water or condensate. Regular inspection using a fibrescope/borescope could prevent such accidents.
A fibrescope or a flexible borescope is a flexible optical inspection device that consists of fibre optic bundles with an eyepiece at one end and a lens at the other.
A fibrescope usually comes in two bundles: (i) a fibre optic light bundle that is for illuminating the object to be investigated, and (ii) a fibre optic image bundle to relay the image to the eyepiece. It allows a direct visual inspection for an otherwise inaccessible part, as observations of remote, difficult-to-reach areas can be made through a video monitor with high-resolution images. The flexible fibres allow it to be manoevred in hard-to-reach or inaccessible areas.
It is often used to verify findings from other tests, such as infrared thermography or impact-echo testing.
Common applications include:
– Inspection of connecting condition behind the external cladding wall of a building.
– Inspection of defects on concrete surface(s) in a deep and narrow gap.
– Determination of corrosion condition of steel tendon(s) inside post-tensioning ducts of pre-stressed structural member(s).
– Investigation of service pipes, ducts and other inaccessible areas.
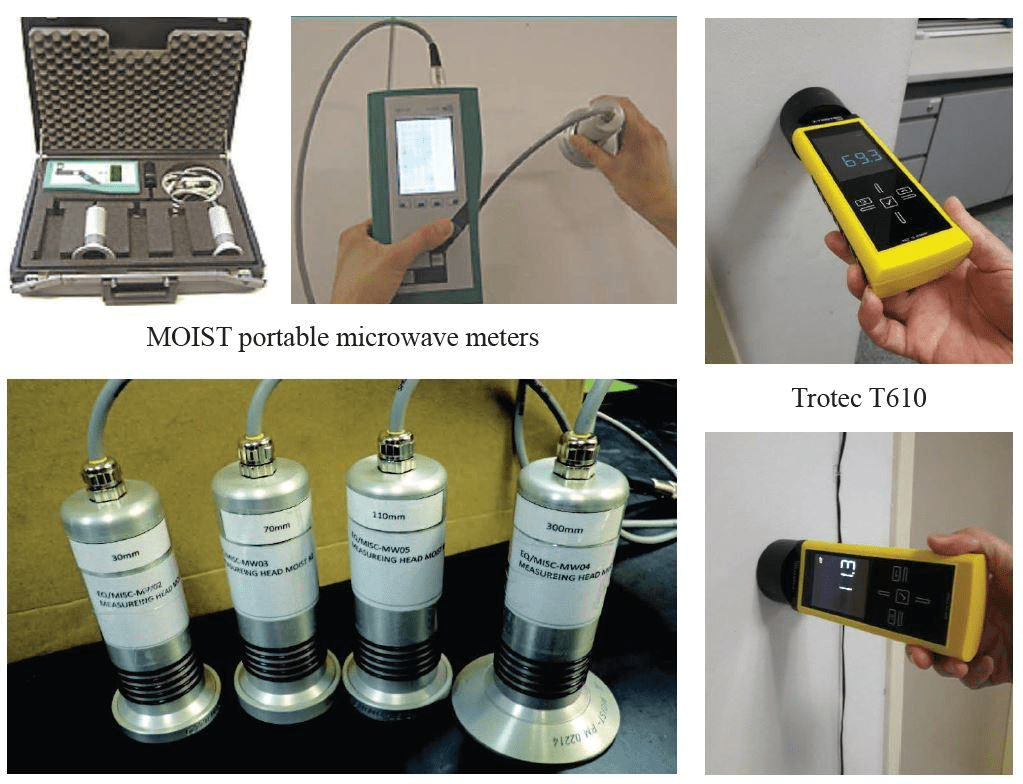
Microwave tomography is a technique to measure the moisture of various materials based on the relatively high dielectric constant of “water” in comparison to the dielectric properties of the material. An electrical field (microwave) is applied to the material, and the microwave induces oscillations of bipolar molecules (i.e., water). Water molecules will reflect and absorb an electrical field during oscillations. A higher electrical field reflected indicates higher water content.
The technique is non-destructive and applicable to wood, brickwork and concrete. The uniqueness of this technique is its ability to measure moisture content at various depths up to 110 mm, allowing the plotting of a 3-D contour of moisture content and facilitating the tracing of the water source.
Thermography can be used to identify the position of water leakages. The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions. Thermo tracer is an advanced equipment used in thermography technology.

Protimeter / Moisture Meter
Moisture meter is used to determine the presence of moisture. Moisture readings can be taken within masonry walls, dry walls, insulation, concrete members, roofing, wood construction, and other building components.
