Case 2 – Concrete Spalling
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Good Practices
Design
Adopt SS EN 1992-1-1, SS EN 1992-1-2, CP 65-1 or equivalent for the design of concrete. (SS 652: A.1.1.1)
Specify admixtures (e.g., water-reducing agent, pozzolanic products, pore refiner, etc.) to reduce permeability. Alternatively, for corrosion control in special areas with a high risk of water penetration, an electrochemical treatment can be specified; a process where electrochemical drying of concrete occurs by passing a current through the reinforcement, similar in principle to cathodic protection in accordance with BS EN 1504-9 or equivalent.
Construction
For the construction of basements, refer to the guidelines and provisions stipulated in BS 8004, EN 1997 or equivalent. Maintain water-cement ratio and the recommended aggregate grading during basement construction. Verify aggregate quality in accordance with ASTM C33/C33M-16e1 or equivalent. Use corrosion-resistant bars and corrosion inhibitors. Apply proper vibration (compaction) and curing. Consider concrete sealing to avoid exposing the aggregate in concrete work (mitigate pitting, scaling, spalling, powdering or chalking of concrete).
Concrete
Design
- Use good quality concrete:
- Cement: Portland cement blended with fly ash and slag to increase permeability
- Aggregate: Rust, silt, clay and sea-salt free. Chlorides in sand <0.06%; chlorides in coarse aggregates <0.03%; sulphates in aggregates <0.4%
- Water: pH< 6; sulphate content <1000 ppm; chloride content <500 ppm
- Concrete mix: cement content < 420 kg/m3; water-cement ratio < 0.45
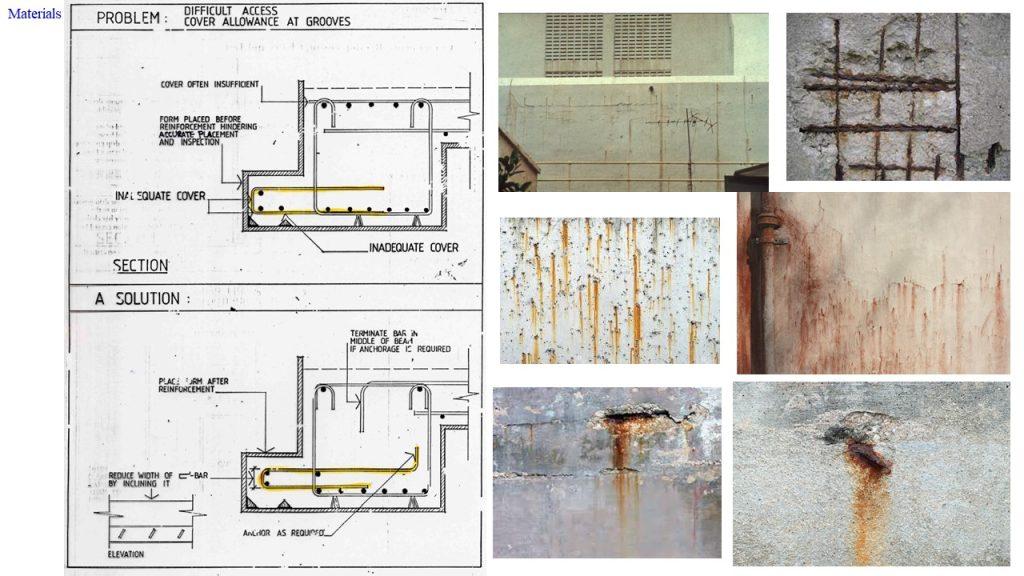
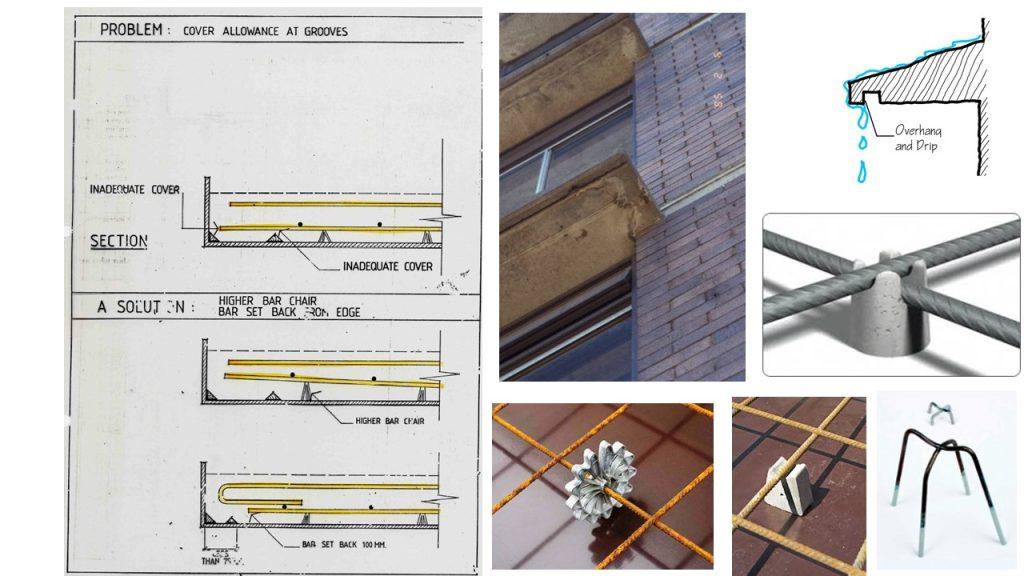
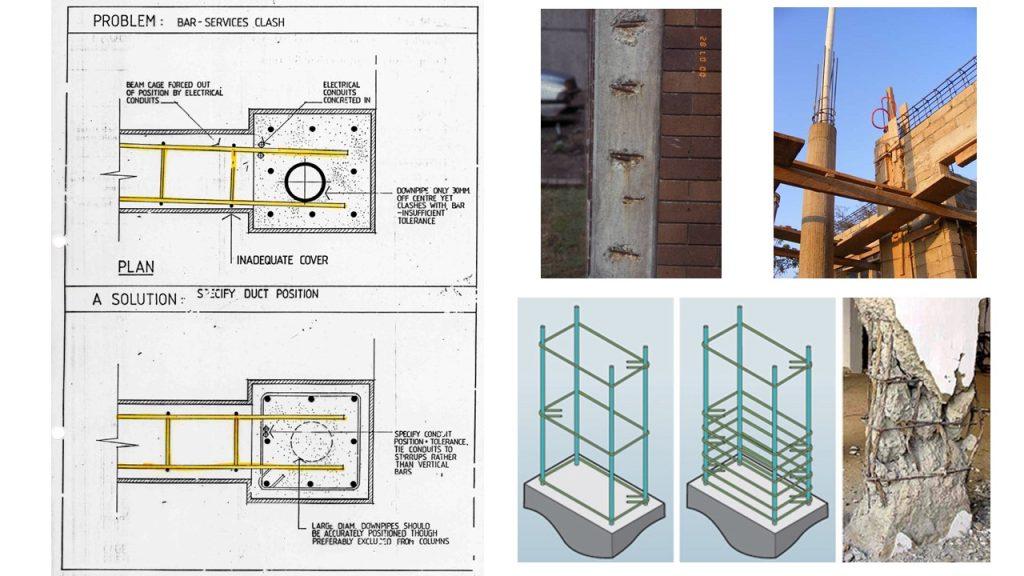
- Ensure that the concrete cover provides sufficient protection against carbonation:

Material
Select appropriate concrete and reinforcement for concrete work.
Construction
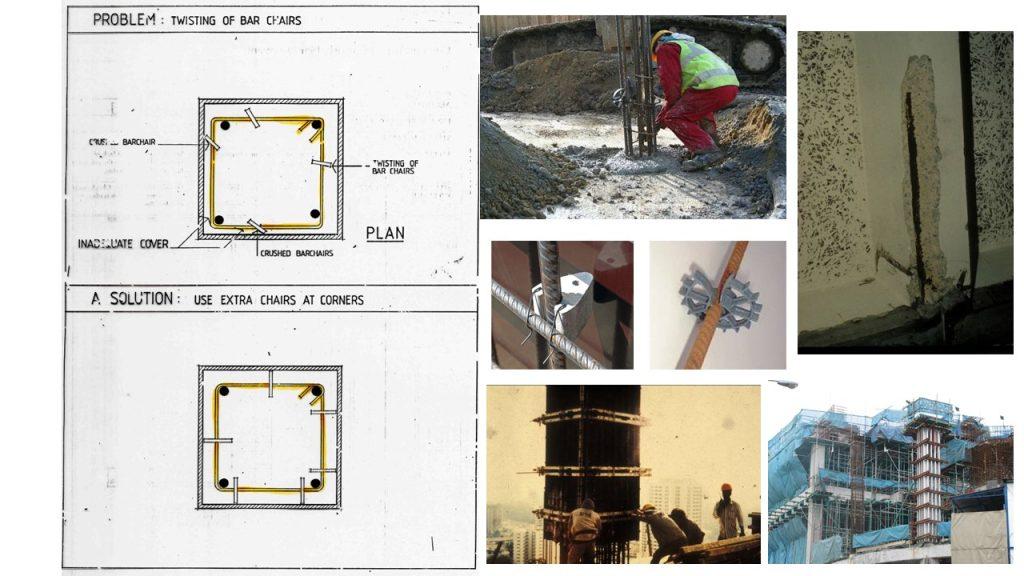
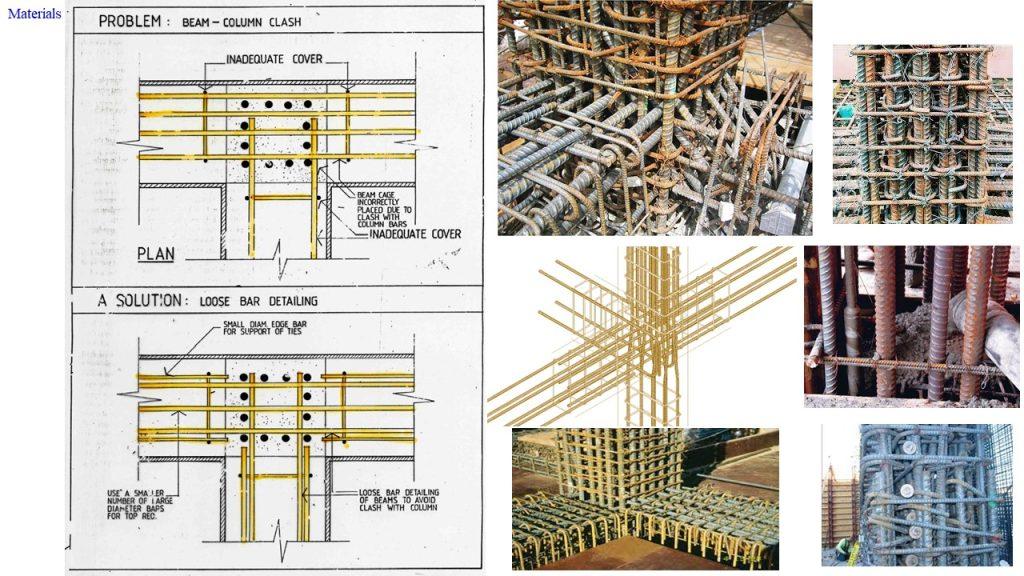
To ensure sufficient concrete cover, concrete spacers or bar chairs.
Reinforcement bars can be protected further by:
1. use of non-metallic coatings such as epoxy coatings or cement based coatings
2. use of metallic coatings such as Zinc and Nickel
3. Cathodic protection
4. use of corrosion inhibitors
5. use of corrosion resistance reinforcement (eg. stainless steel)
Ensure thorough compaction of the concrete during placement to obtain dense concrete minimizing carbonation.
Quality Control
Check for the quality of concrete before placing. e.g. water cement ratio, slump test, etc.
Check for the correct concrete cover thickness.