Penicillium
 Species of the Penicillium can be both saprophytic and parasitic. Thus occupants may form ideals hosts for fungal growths of Penicillium. Growth on agar shows a colony center greenish with white edges.
Species of the Penicillium can be both saprophytic and parasitic. Thus occupants may form ideals hosts for fungal growths of Penicillium. Growth on agar shows a colony center greenish with white edges.
Features
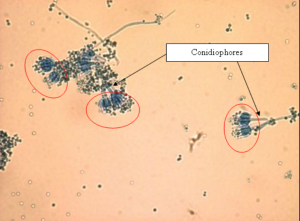
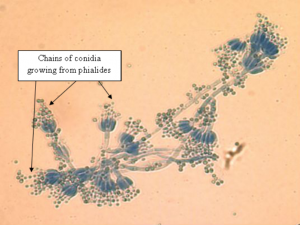
Conidia and conidiophores of the Penicillium are transparent or brightly coloured. Clusters of phialides are observed at the tip of conidiophores bearing resemblance to a brush. These phialides each produce a chain of conidia. The conidia are 1-celled, with the shape ranging from round to oval.
| Pigment Colour of Fungus |
|
| Observed Spores Growth |
|
| Spore Characteristics |
|
Allergenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas |
Forms/ Medical Terms |
Descriptions |
|
Airway to Lungs (Bronchial Tubes) |
Asthma |
|
|
Lungs |
Allergic Alveolitis
|
|
|
Nose |
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS) |
|
Pathogenic Diseases
| Categories | Form/Medical Terms | Descriptions |
| Eyes
|
Keratitis | Cornea inflammation, usually after wounding or injuring the cornea |
| Endophtalmitis | Inflammation internal eyeball tissue structures | |
| Ears | Otomycosis | Inflammation of the ear canal |
| Digestive Tract | Esophagitis | Inflammation of the esophagus, or food passage to the stomach, causing the death of the membrane tissue |
| Bone | Osteomyelitis | Inflammation of bone and bone marrow |
| Respiratory Tract | Pneumonia | Lung inflammation |
| Heart
|
Endocarditis | Inflammation of the internal membrane of the heart |
| Pericarditis | Inflammation of the membrane sac enclosing the heart | |
| Systematic Infection | Penicilliosis |
|
| Other | · Inflammation of abdomen or abdominal organs
· Urinary tract infections |