Chip
During normal operation, optical performance of LEDs gradually decreases during lifetime. In turn, this means a limitation in lifetime. Performance decrease is caused by growing defects in the epitaxy layers or on their boundaries, resulting in an increase of not radiating recombination and a decrease of optical efficiency. Usually a 30% or 50% decrease of optical performance is defined as defect while expected operation life is between 20,000 h and 100,000 h.
Ageing due to extension of defects is considerably dependent on junction temperature Tj and current. Therefore, a sufficient control of these parameters is imperative for reaching expected lifetime. Accelerated ageing, i.e. LED efficiency loss within a period lower than expected life, is caused by adverse factors like low quality of epitaxy layers as well as, often, an excess junction temperature due to insufficient heat dissipation. Furthermore, penetration of humidity or other contaminants, latent ESD (Electro Static Discharge) damage as well as an instable power supply can result in an accelerated degradation of epitaxy layers13.
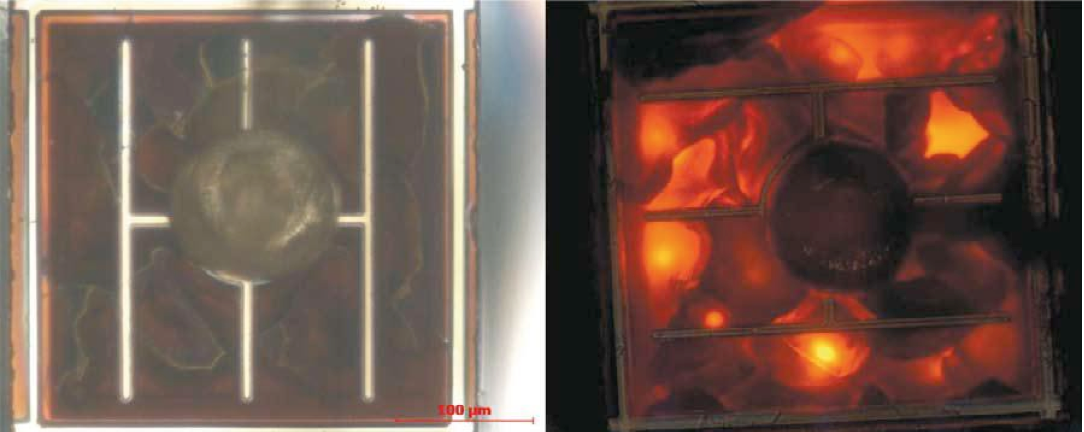
Figure 1 Chip Failure
Source: LED professional, 2010
A catastrophic defect like a sudden failure can be caused by ESD or EOS (Electrical Over Stress) due to electrical overload resulting in a serious damage of the epitaxy layer13.
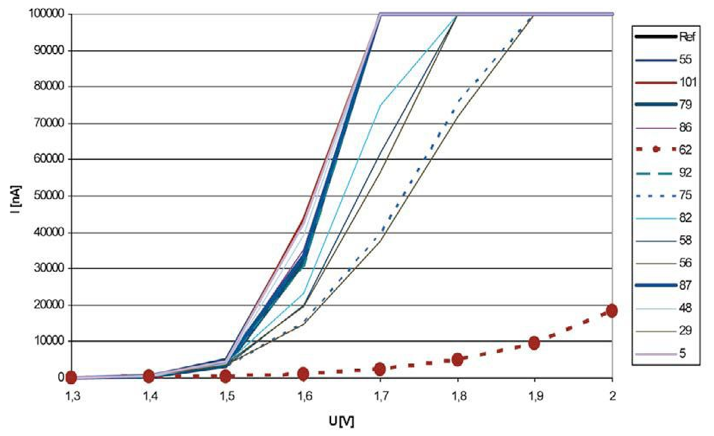
Figure 2 General characteristics (current/ voltage diagram) for different diode types
Source: LED professional, 2010