Curvularia
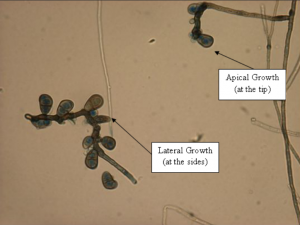
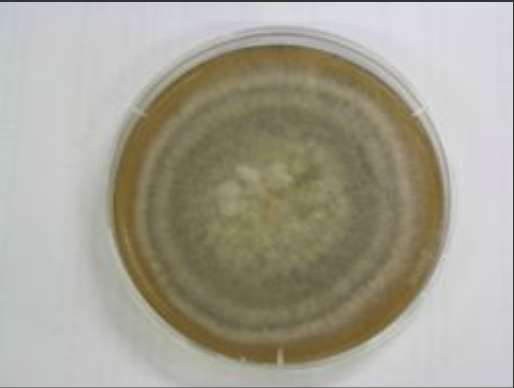 Curvularia species were present in 17% of the samples collected in the study. Colony on agar shows white woolly vegetation with shades of greenish-brown. The spores or conidia of the fungus contain dark pigment, which is especially observable when the spores mature. Such spores can grow from the tips or sides of hyphae.
Curvularia species were present in 17% of the samples collected in the study. Colony on agar shows white woolly vegetation with shades of greenish-brown. The spores or conidia of the fungus contain dark pigment, which is especially observable when the spores mature. Such spores can grow from the tips or sides of hyphae.
Features
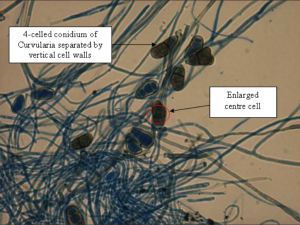
Distinctive features of Curvularia lies in the conidia. It is subdivided into generally 3 to 5 cells per conidium separated by vertical cell walls along the length of the conidia. One centre cell is abnormally larger than the other subdivided cells. Mature conidia display a slightly bent curvature, narrowing at the 2 ends.
Curvularia can is both saprophytic and parasitic, making them possibly infectious to man.
| Pigment Colour of Fungus |
|
| Observed Spores Growth |
|
| Spore Characteristics |
|
Allergenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas |
Forms/ Medical Terms |
Descriptions |
|
Airway to Lungs (Bronchial Tubes) And Lungs |
Asthma |
|
|
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Fungal Disease (ABPFD)
|
|
|
|
Eyes
|
Allergic Rhinitis |
|
|
Throat |
||
|
Nose |
||
|
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS) |
|
Pathogenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas |
Forms/ Medical Terms |
Descriptions |
|
Eyes (Corneal) |
Keratitis |
|
|
Skin (Cutaneous) |
Dermatomycosis |
|
|
Onychomycosis |
|
|
|
Beneath the Skin (Subcutaneous) |
Mycetoma |
|
|
Respiratory tract |
|
|
|
Brain |
Cerebritis |
|
|
Cerebral Abscess
|
|
|
|
Heart |
Endocarditis
|
|
|
Others |
Peritonitis |
|