Stachybotrys
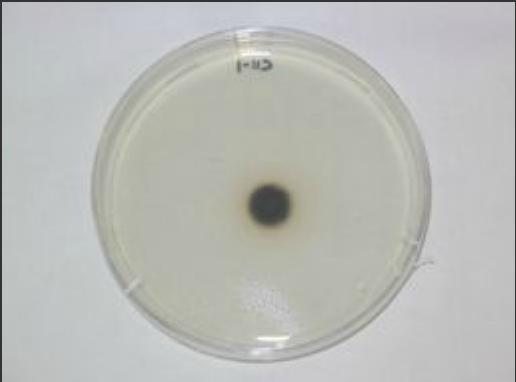 Stachybotrys is mainly saprophytic, thus will not infect the human body. However allergic reactions and toxic poisoning have been associated to the fungus. Growth on agar shows a colony centre brownish black with white edges.
Stachybotrys is mainly saprophytic, thus will not infect the human body. However allergic reactions and toxic poisoning have been associated to the fungus. Growth on agar shows a colony centre brownish black with white edges.
Features
Dark pigmented spores and conidiophores (special hyphae linking spores to vegetation) can be observed of the fungus. Clusters of short slender cells can be seen at the tips of the conidiophores, termed phialides. These phialides each produce a single conidium. The conidia are 1-celled, ranging from brown to black depending on age. The shape of the conidia ranges to round to oval.
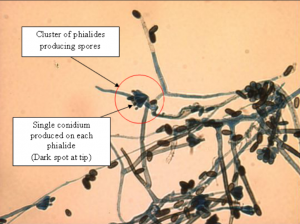
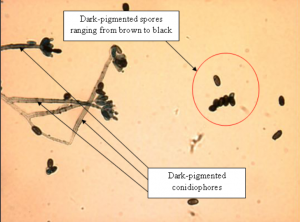
| Pigment Colour of Fungus |
|
| Observed Spores Growth |
|
| Spore Characteristics |
|
Allergenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas |
Forms/ Medical Terms |
Descriptions |
|
Airway to Lungs (Bronchial Tubes) |
Asthma |
|
|
Eyes |
Allergic Rhinitis |
|
|
Throat |
||
|
Nose |
Pathogenic Diseases
| Affected Areas | Form/Medical Terms | Descriptions |
| Lungs (Infants)
|
Pulmonary Hemorrhage | Profuse bleeding of the lungs |
| Pulmonary Hemosiderosis | Proteins are abnormally accumulated in tissue | |
| Others | Stachybotryotoxicosis |
Symptoms are:
|