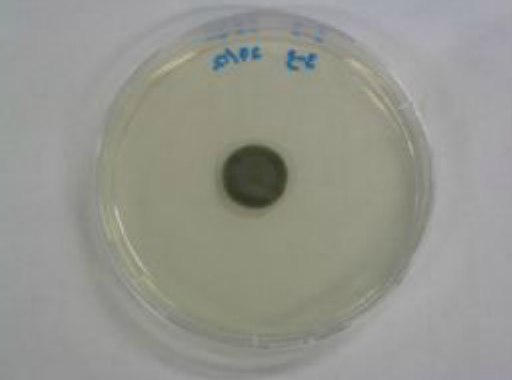
 Aspergillus accounts for a significant number of fungal species for microfungi. While colours of the fungus varies accordingly to its species, growths on agar for the study shows a light green colony center with white edges.
Aspergillus accounts for a significant number of fungal species for microfungi. While colours of the fungus varies accordingly to its species, growths on agar for the study shows a light green colony center with white edges.
Features
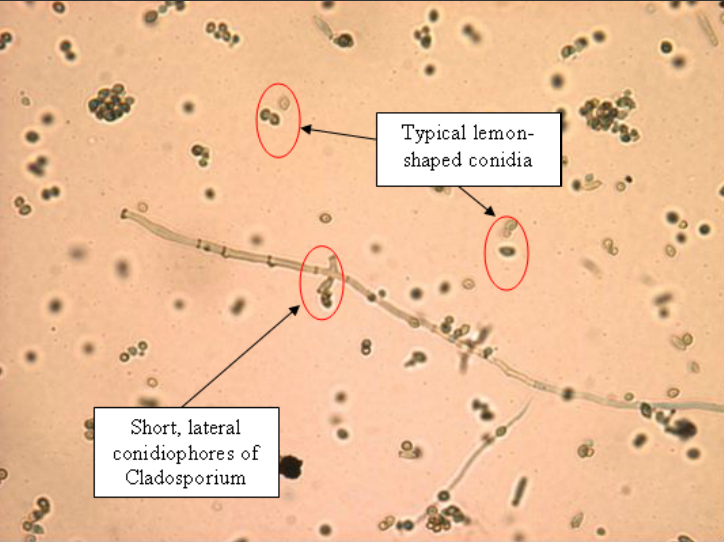 Cladosporium is a fungus with dark-pigmented conidiophores and conidia. Similar to curvularia, spores sprout direct from the short conidiophores, which are located at apically and laterally of hyphae. The conidia are 1 to 2-celled, with the shape ranging from round to oval. Lemon-shaped conidia are also characteristic of Cladosporium spores.
Cladosporium is a fungus with dark-pigmented conidiophores and conidia. Similar to curvularia, spores sprout direct from the short conidiophores, which are located at apically and laterally of hyphae. The conidia are 1 to 2-celled, with the shape ranging from round to oval. Lemon-shaped conidia are also characteristic of Cladosporium spores.
| Pigment Colour of Fungus |
- Dark-coloured (Spores and conidiophores)
|
| Observed Spores Growth |
- At tip (Apical) and side (Lateral)
|
| Spore Characteristics |
- 1 to 2-celled
- Shape from round to oval, lemon-shaped common, usually in chains
|
Allergenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas
|
Forms/ Medical Terms
|
Descriptions
|
|
Airway to Lungs (Bronchial Tubes)
|
Asthma
|
- Inflammation and constriction of airway to lung
|
|
Eyes
|
Allergic Rhinitis
|
- Occurs when allergens trigger release of histamine, causing inflammation and fluid production in linings of nasal passages, sinuses, and eyelids
- Reactions include sneezing, congestion, runny nose, itchy nose, throat, eyes, and ears
|
|
Throat
|
|
Nose
|
|
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS)
|
- Occurs in individuals with a background of asthma and rhinitis
- Does not invade tissue; fills up sinus with substances of membrane cells, decomposing white blood cells and fungal hyphae
- Built-up pressure in the sinus can eventually cause expansion and erosion of the sinus walls
|
|
Affected Areas
|
Forms/ Medical Terms
|
Descriptions
|
|
Airway to Lungs (Bronchial Tubes)
|
Asthma
|
- Inflammation and constriction of airway to lung
|
|
Skin
|
|
- Sensitization and reactivity of the skin to airborne cladosporium
|
|
Eyes
|
Allergic Rhinitis
|
- Occurs when allergens trigger release of histamine, causing inflammation and fluid production in linings of nasal passages, sinuses, and eyelids
- Reactions include sneezing, congestion, runny nose, itchy nose, throat, eyes, and ears
|
|
Throat
|
|
Nose
|
|
Allergic Fungal Sinusitis (AFS)
|
- Occurs in individuals with a background of asthma and rhinitis
- Does not invade tissue; fills up sinus with substances of membrane cells, decomposing white blood cells and fungal hyphae
- Built-up pressure in the sinus can eventually cause expansion and erosion of the sinus walls
|
Pathogenic Diseases
|
Affected Areas
|
Forms/ Medical Terms
|
Descriptions
|
|
Eyes
(Corneal)
|
Keratitis
|
|
|
Skin
(Cutaneous)
|
Chromomycosis
|
- Chronic infection
- Rough, irregular wounds can be observed
|
|
Onychomycosis
|
- Thickening, roughening, and splitting of nails due to infection
|
|
Skin Lesion
|
- Infection that leaves wounds on the skin
|
|
Beneath the Skin
(Subcutaneous)
|
Mycetoma
|
- Chronic skin infection that goes beyond the skin
- Usually on the leg
- Discharges of oily pus can be observed
|
|
Brain
|
Cerebral Abscess
|
- Pus collection in the brain due to inflammation and tissue disintegration
- Termed Cladosporiosis when the disease is opportunistic, occurring due defect of the nervous system
|
 Aspergillus accounts for a significant number of fungal species for microfungi. While colours of the fungus varies accordingly to its species, growths on agar for the study shows a light green colony center with white edges.
Aspergillus accounts for a significant number of fungal species for microfungi. While colours of the fungus varies accordingly to its species, growths on agar for the study shows a light green colony center with white edges. Cladosporium is a fungus with dark-pigmented conidiophores and conidia. Similar to curvularia, spores sprout direct from the short conidiophores, which are located at apically and laterally of hyphae. The conidia are 1 to 2-celled, with the shape ranging from round to oval. Lemon-shaped conidia are also characteristic of Cladosporium spores.
Cladosporium is a fungus with dark-pigmented conidiophores and conidia. Similar to curvularia, spores sprout direct from the short conidiophores, which are located at apically and laterally of hyphae. The conidia are 1 to 2-celled, with the shape ranging from round to oval. Lemon-shaped conidia are also characteristic of Cladosporium spores.