Case 4
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
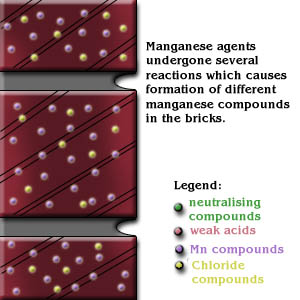
Cause of Defects
Conditions for lime blooming to occur:
- Soluble salts must be present within the free cement in mortar.
- There also should be a source of water and it must be in contact with the salts for sufficient time to permit them to dissolve.
- The masonry should be such that the migration of salt solutions to the surface, or other locations, occurs in an environment which is conducive to the evaporation of water.
- The salt solutions may migrate across surfaces of units, between the mortar and units, or through the pore structure of the mortar or the masonry units.
- When regular powdery efflorescence goes through cycles of being deposited on the surface re-dissolved when new water occurs- drying our new water-etc. It can form crystals. These crystals become tightly bonded to the surface.
- Lime staining due to leaching out of calcium compounds which form patches of white carbonates (recognizable by solubility in acid and evolution of carbon dioxide bubbles). Lime stains can be more difficult to remove than efflorescence, often requiring chemical treatment.
Possible sources of water:
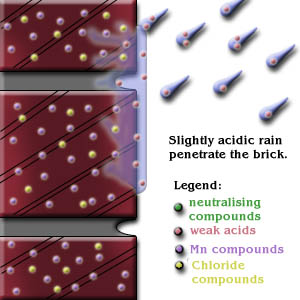
a) Rainwater
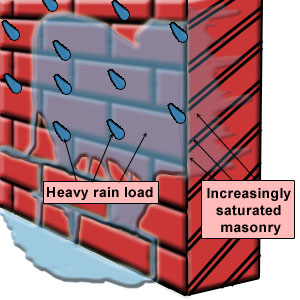
The primary source of moisture for the occurrence of efflorescence is rain water which penetrates or comes in contact with masonry. Water film adheres to the external surfaces of wall and migrates via capillarity through the brickwork (Figure 2).
The presence of this free water in mortar joints could lead to the dissolution of alkaline salts available.Upon drying lime from the mortar is brought to the surface.
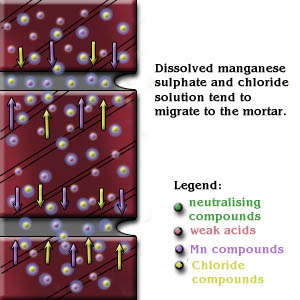
b) Rising dampness
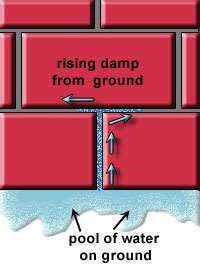
From the picture, the lime bloom occurs not far from the ground DPC level. Another possible contributing factor of moisture is ground water carried up a wall (Figure 3).
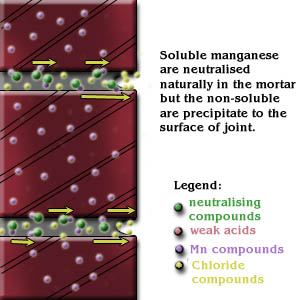
c) Condensation
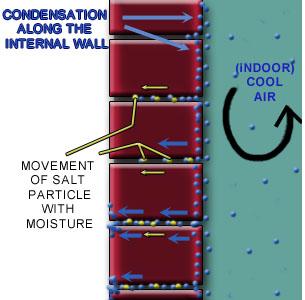
In addition to rainwater and groundwater, water may accumulate within the wall as a result of condensation of water vapor.
Condensation is usually due to moisture originating inside buildings. Cold air from internal air con unit may condense on the interior surface.This gain in moisture content increases the vapor pressure of the inside air substantially above that existing outdoors. This increased pressure tends to drive the vapor outwardly from the building interior through any vapor-porous materials that may comprise the enclosing surfaces.
When vapor passes through porous and homogeneous materials, mortar in this case, which may be warm on one side and cold on the other, encourages condensation. This condensed moisture can contribute to lime leaching on the mortar joints.