Car vibration, jerky movement
- Description of defect
Strong jerk cause discomfort in rides and it is significantly affect the electrical and mechanical subsystem performance and eventually reduce the system’s expectancy life usage. Uncomfortable ride is also a sign of faulty in the bearings. Loose bearings, worn and rusty is a sign of inadequate inspection to the bearings.
Vertical car vibration
- Causes
Vertical car vibrations can be produced from the drive and frequency converter that transferred to the elevator car through the traction media.
Lateral car vibrations
- Causes
- Guide rail misalignment;
Most significant contributor to lateral vibrations of elevator ride - Guide roller configuration;
Configuration of guide rollers affect quality ride of elevators where an eccentric or flat spot have different effects depending on the size of roller and speed of the car - Static balance of car frame;
The static balance of car frame, which is the geometry will affect the elevator ride quality. The movement of the car whether it is travelling across the guide rail bracket fixing positions or it travels between the guide rail brackets will have impact to deflection of the guide rail - Lift well configuration and air displacement;
The speed of the car travels in the hoistway affect the ability of the air pressure that created to be displaced. Wind velocity that created when a lift travel in a hoistway will exert a pressure on the sides of the car and the pressure varies as it passed a divider beam, sill plate or counterweight frame. It also caused the landing doors to be pushed towards the lobby side. When the car passes a floor, pressure on the well side of the entrance is immediately reduced, causing the landing doors to be pulled back towards the hoistway. These pulsations create a combination of discomfort motions - Car speed;
As the car speed increases, the effects on guide roller, alignment of guide rail and air displacement will increased
- Diagnostic/testing method (for vibrations)
Elevator vibration analysis is a method to measure ride quality for elevator. The hardware tool system combined with a software will allow the technicians to measure vibration and sound and the measured value shall be referred with the ride quality standards, such as ISO 18738:2012

Physical Measurement Technologies EVA-625 Elevator Vibration Analysis system [6]
- Good practices (for vibrations)
The unit for vibration is mili-g (mg), and one mg equals ca. 0.01 m/s².
For lateral vibrations, the standards required:
- ≤ 15 mg (ISO MPtP)
- ≤ 10 ±3 mg (ISO A95)
For vertical vibrations, the standards required:
- ≤ 25 mg (ISO MPtP)
- ≤ 15 ±5 mg (ISO A95)
The following standards are applicable to be referred for vibrations ride quality
- ISO 2631-1-1997 – Mechanical vibration and shock –Evaluation of human exposure to whole-body vibration – Part 1: general requirements
- ISO 18738:2003 – Lifts (elevators)- Measurements of lift ride quality
- ISO8041:1990 and Amd.1:1999 Human response to vibration – Measuring instrumentation
- Corrections
To avoid discomfort motion of rides, in the case where displacement of air pressure in the hoistway created lateral vibrations, the hoistway shall have a clear area at least 15% of the car platform area for lift speeds up to 5 m/s and this figure shall be increased by 5% for each additional 0.5 m/s increase in car speed.
To reduce lateral vibration produced from the roller guide, it is recommended to use Electric Active Roller Guide that reduces vibration produced by 50%. It comprised with an accelerometer that detect car vibration during operation, and the actuators will cancel the vibration through a controlled electromagnetic force
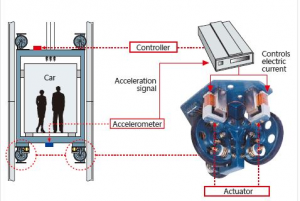
Electric Active Roller Guides [7]