Case 1
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Carry out inspection to determine the current roof condition and document visible evidence of water leakage. Indications of wear and tear, maintenance, attempted repairs, damage from non-weatherrelated causes, such as impacts or structural movements, are to be recorded in accordance with ASTM D7053/D7053M-17. Sealants can crack/lose adhesion at its interface under solar radiation.
Carry out inspection to determine the current roof condition and document visible evidence of water leakage. Indications of wear and tear, maintenance, attempted repairs, and damage from nonweather-
related causes, such as impacts or structural movements, are to be recorded in accordance with ASTM D7053/D7053M-17. Sealants can crack/lose adhesion at its interface under solar radiation.
Check for roof leaks yearly, especially at roof penetrations, in accordance with ASTM E241-09. Use
thermography to identify the position of water leakages on the roof. Maintain gutters and downspouts to enable free/undisrupted flow of water and keep them clear of leaves and other debris to avoid exposure to excessive roof runoff and eventual leakage.
Review work orders and purchase orders for building maintenance and other activities that may relate to water leakage problems. Maintain service history: the known performance record of the roof system, including the physical symptoms of water leakage, progression of leakage behaviour, maintenance and repair history, extent and locations of leakage, etc., in accordance with ASTM D7053/D7053M-17.
Design repair materials/methods to manage environmental factors (e.g., chemical/physical/mechanical
conditions). Adopt the specifications of grouting materials for repair as set under ISO/TR 16475.
Flat roofs should be screeded to fall and be periodically inspected for any ponding. Visual observations
of free-flowing water towards the outlets should be made to ensure that the water drains off thoroughly so as to avoid leftover ponding in the gutter or on the reinforced concrete flat roof in accordance with BS
8221-1, SS 509-1 or equivalent. Free flow in gutters and downspouts should be maintained. They should
be kept clear of leaves and other debris.
Diagnostics of Defects (see also NDT)
Thermography
Thermography can be used to identify the position of cracks. A range of crack widths, representing mechanical damage, has been induced under controlled laboratory conditions. The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions.
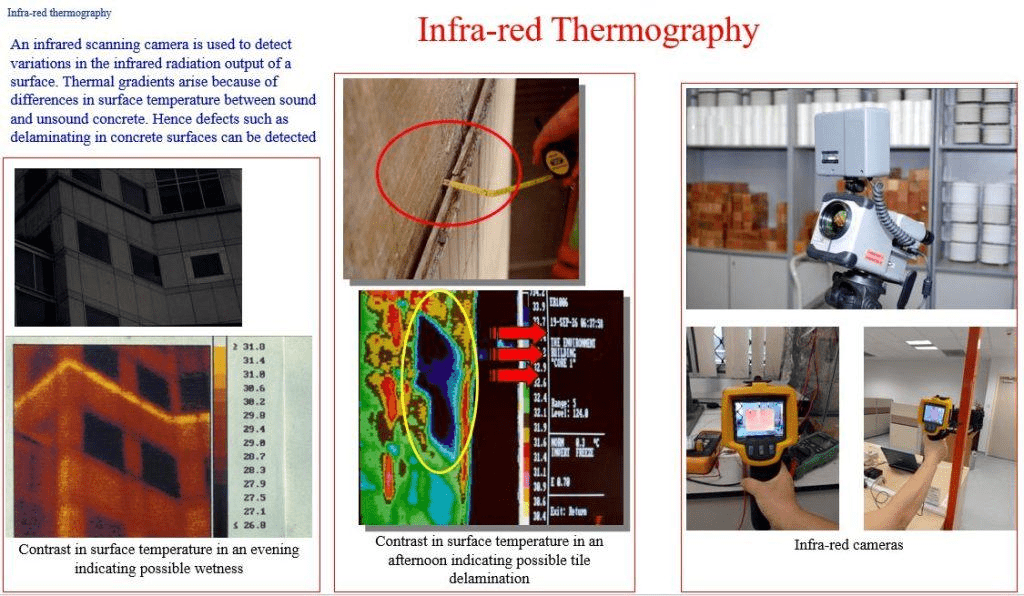
The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions. Thermo tracer is an advanced equipment used in thermograph technology.
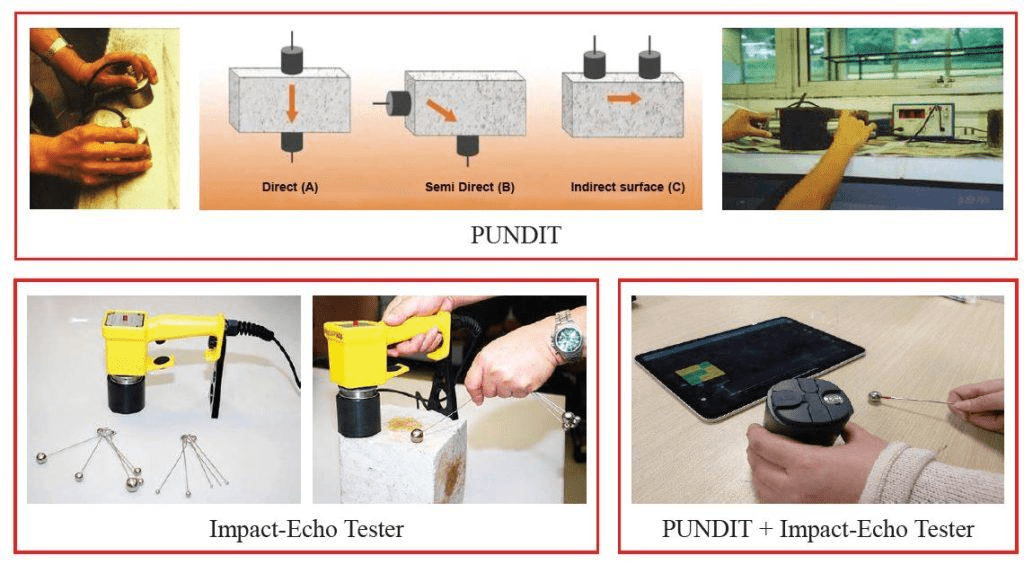
Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity (UPV)
UPV can identify non-homogeneous conditions such as voids, cracks and honeycombs using the optional hand-held terminal. This method can also be used to estimate the depth of cracks.
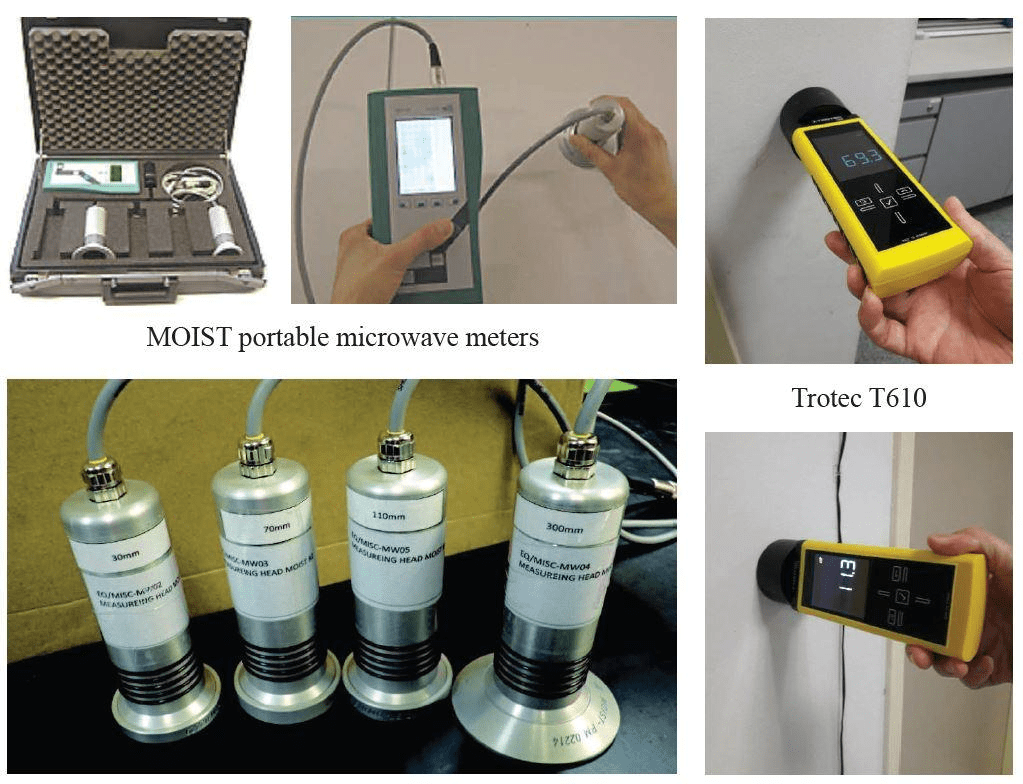
Microwave tomography is a technique to measure the moisture of various materials based on the relatively high dielectric constant of “water” in comparison to the dielectric properties of the material. An electrical field (microwave) is applied to the material, and the microwave induces oscillations of bipolar molecules (i.e., water). Water molecules will reflect and absorb an electrical field during oscillations. A higher electrical field reflected indicates higher water content.
The technique is non-destructive and applicable to wood, brickwork and concrete. The uniqueness of this technique is its ability to measure moisture content at various depths up to 110 mm, allowing the plotting of a 3-D contour of moisture content and facilitating the tracing of the water source.