Case 1
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Carry out regular cleaning by chemical and mechanical applications (e.g., alkaline or solvent cleaning
agents, hydrofluoric acid, air or water abrasive cleaning) and clear dirt regularly in accordance with SS 509-1, BS 8221-1 or equivalent. Remove moulds, lichens and other growths with a stiff brush and treat the residue with biocide chemicals. Use paint, which does not support mould growth. If affected, remove infected paint and sterilise the surface by applying a fungicide solution/algaecide solution to prevent recurrence in accordance with BS 6150, BS EN ISO 1513, SS 542 or equivalent.
Periodic re-painting (about 5-7 years period) is necessary so as to keep the surface free from such peeling.
Diagnostics of Defect (see also NDT)
Visual Inspection
Conduct a comprehensive visual inspection.
The following tests can be used to assist with the diagnosis:
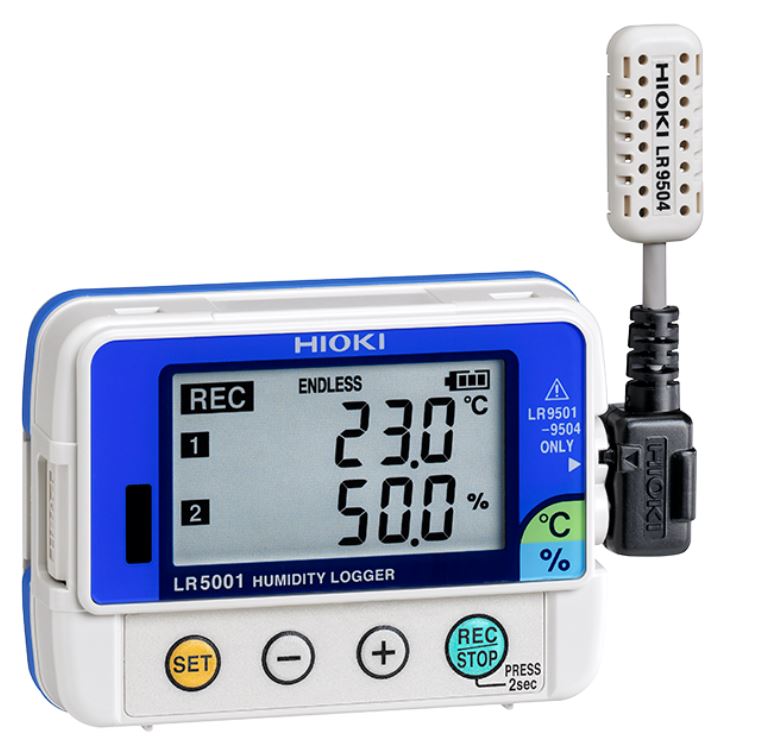
Hygrometer
Hygrometer can be used to test the amount of moisture present in the structure.



Thermography can be used to identify the position of cracks. A range of crack widths, representing mechanical damage, has been induced under controlled laboratory conditions. The method is based on the characteristics of heat flow phenomenon, in a conductive medium of specific geometry, which is intended to model predetermined boundary conditions.

Microwave tomography is a technique to measure the moisture of various materials based on the relatively high dielectric constant of “water” in comparison to the dielectric properties of the material. An electrical field (microwave) is applied to the material, and the microwave induces oscillations of bipolar molecules (i.e., water). Water molecules will reflect and absorb an electrical field during oscillations. A higher electrical field reflected indicates higher water content.
The technique is non-destructive and applicable to wood, brickwork and concrete. The uniqueness of this technique is its ability to measure moisture content at various depths up to 110 mm, allowing the plotting of a 3-D contour of moisture content and facilitating the tracing of the water source.
