Case 1
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Cause of Defects
The cracking of concrete wall is probably caused by one of the following factors or the combination of several factors [1-5]:
- Differential structural movement; such as the joint between column and wall
- Differential settlement of foundation;
- Structural deficiency;
- Drying shrinkage of cementitious materials;
- Volumetric changes;
- Direct stress;
- Flexural stress;
- Thermal shock caused by heat gain and sudden cooling from rain.
Material compatibility between the plastering and the substrate of an external wall is hence crucial as they are exposed to harsh environment and subjected to stresses caused by differential movements due to cyclical loading, thermal shock, as well as temperature and moisture variation resulting from rains, thunderstorms, solar heat and humidity.

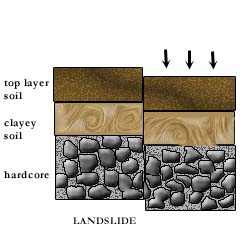
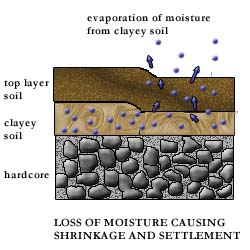
Cracking in this case might be due to differential settlement of the ground with respect to the building. Movements of ground may be due to factors such as subsidence, landslip or moisture changes of shrinkable clay (Figure 1a to d). The backing wall is also suspected to have cracked in tandem with the plaster.
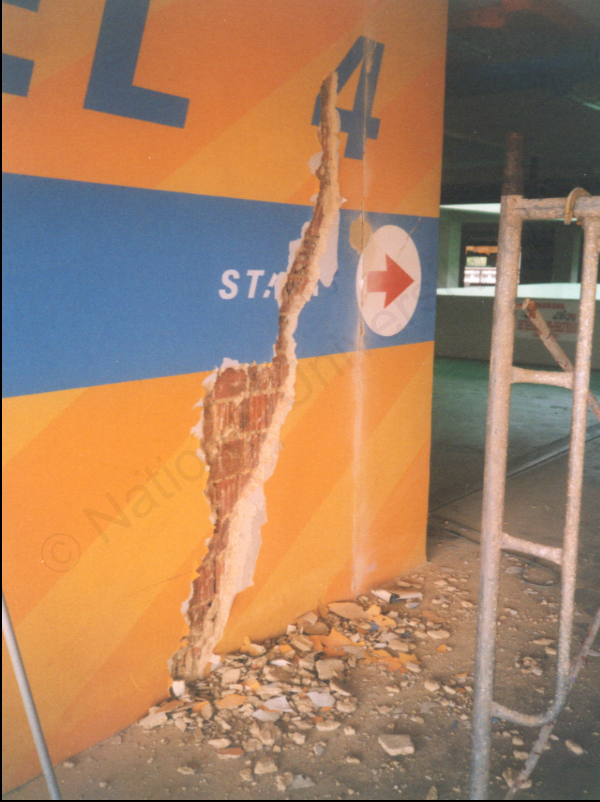

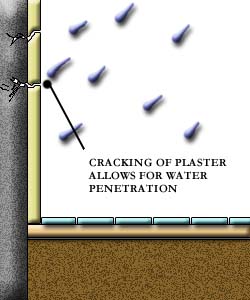
If the cracks in the rendering correspond with cracks in the walls it is likely that these are the roots of the defect and the cause of the cracking of the walls should be ascertained. See Figure 2 above.
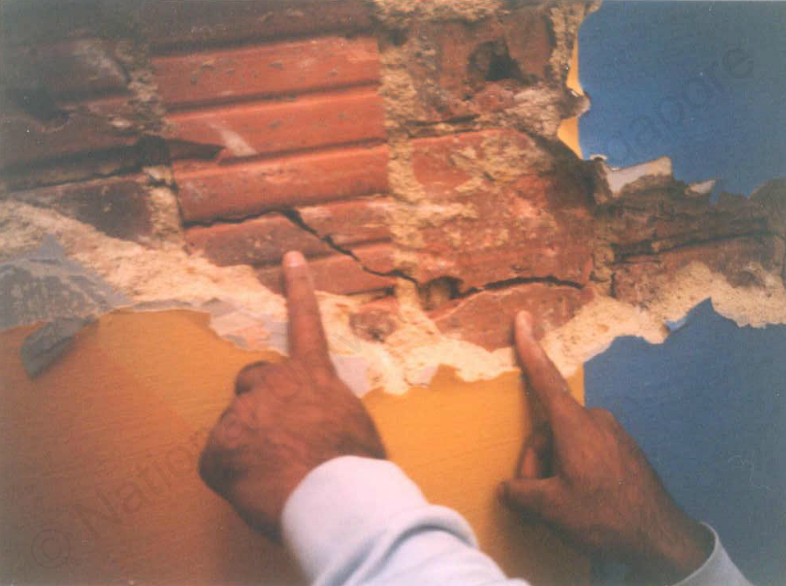

If cracking happens to both the plaster and backing wall, water seepage into the building might take place and interior flooring might be damaged.