Case 3
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Good Practices
Concrete
Design
- Use good quality concrete:
- Cement: Portland cement blended with fly ash and slag to increase permeability
- Aggregate: Rust, silt, clay and sea-salt free. Chlorides in sand <0.06%; chlorides in coarse aggregates <0.03%; sulphates in aggregates <0.4%
- Water: pH< 6; sulphate content <1000 ppm; chloride content <500 ppm
- Concrete mix: cement content < 420 kg/m3; water-cement ratio < 0.45
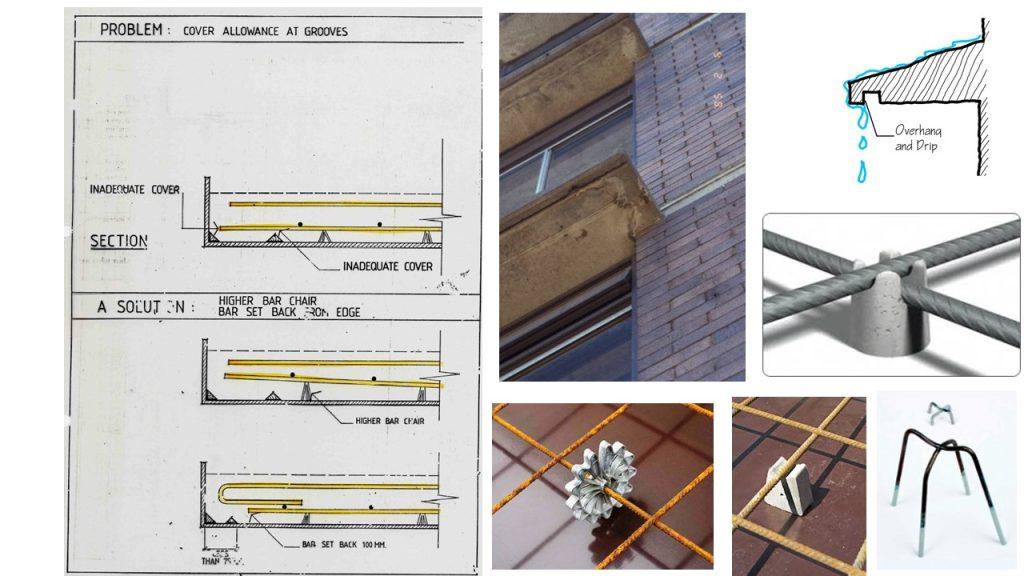
- Ensure that the concrete cover provides sufficient protection against carbonation:
| Condition of exposure | Nominal cover | ||||
| Mild | 25 | 20 | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Moderate | – | 35 | 30 | 25 | 20 |
| Severe | – | – | 40 | 30 | 25 |
| Very severe | – | – | 50 | 40 | 30 |
| Most severe | – | – | – | – | 50 |
| Abrasive | – | – | – | see note 1 | see note 1 |
| Maximum free water/cement ratio | 0.65 | 0.60 | 0.55 | 0.5 | 0.45 |
| Minimum cement content (kg/m3) | 275 | 300 | 325 | 350 | 400 |
| Lowest grade of concrete | C30 | C35 | C40 | C45 | C50 |
| 1) This table relates to normal-weight aggregate of 20mm nominal size. Adjustments to minimum cement contents for aggregates other than 20 mm nominal maximum size are detailed in BS 5328: Part 1. | |||||
Limiting values of the nominal cover of normal weight aggregate concrete
Material
Select appropriate concrete and reinforcement for concrete work.
Construction
Ensure that the concrete mix is appropriate for construction and comply to the specifications specified. If the concrete is ready mix, it shall comply with SS 289.
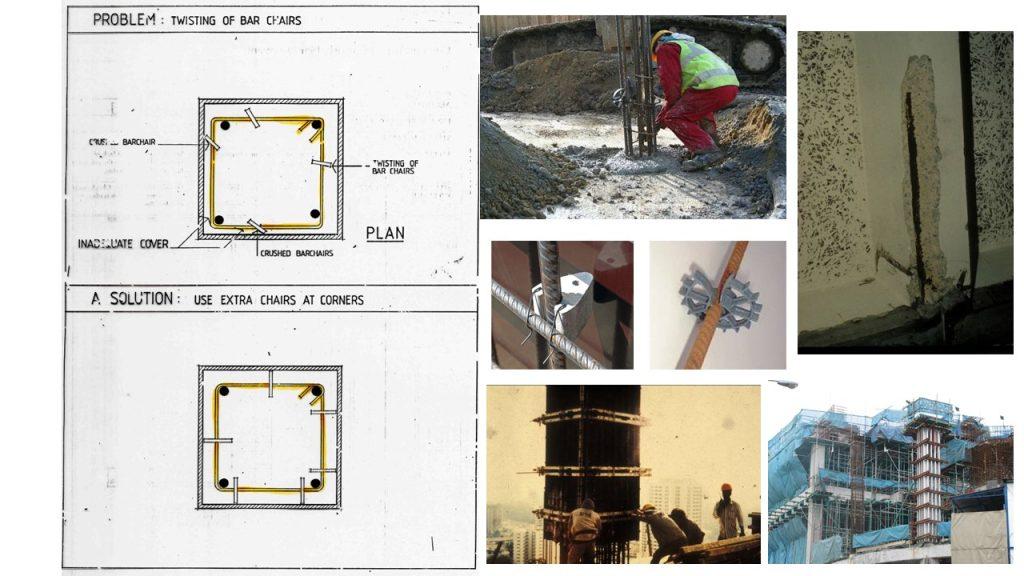
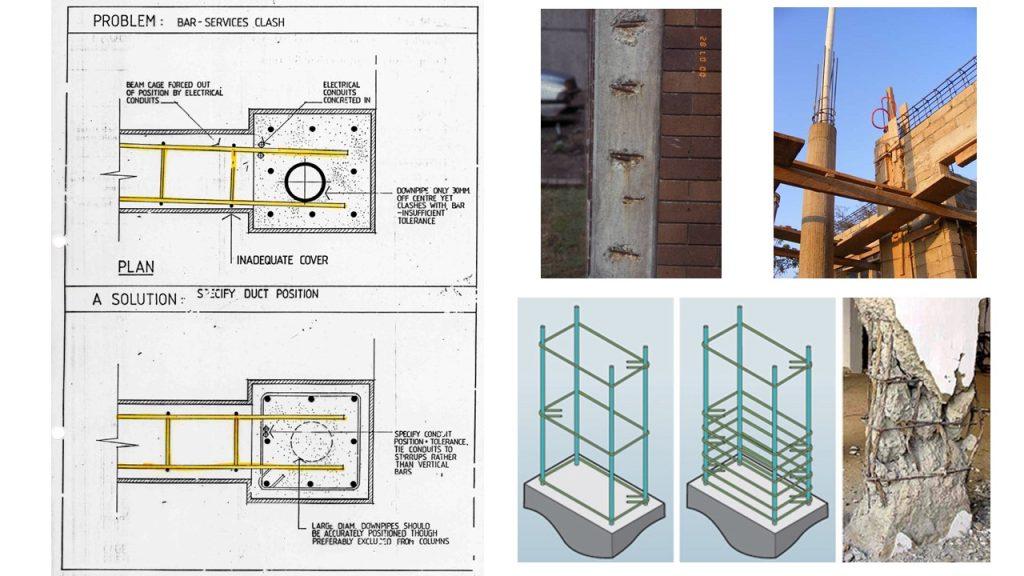
Reinforcements should be laid properly under supervision of consultant engineers and removal of rust and mill scale is important before embedment. During concrete casting, concrete spacers (Figure 1) and bar chairs (Figure 2) are necessary to support reinforcement bars at 600mm distance apart to ensure that the concrete cover is sufficient.
Reinforcements can be further protected by using following methods,
1. use of non-metallic coatings such as epoxy coatings or cement based coatings
2. use of metallic coatings such as Zinc and Nickel
3. Cathodic protection
4. use of corrosion inhibitors
5. use of corrosion resistance reinforcement (eg. stainless steel)
Ensure thorough compaction of the concrete during placement.
Quality Control
- Check for the quality of concrete before placing. e.g. water cement ratio, slump test, etc.
- Check for the correct concrete cover (the thickness of the concrete from the surface to the reinforcement).