Case 3
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Remedial (see also Remedial)
Grout Injection
Small areas of hollow tiles may be repaired without the need to remove the tiles:
-Identify spots of hollow tiles using a tapping test
-Mark the locations clearly
-Drill holes within the joint width closest to the hollowness
-Vacuum clean dust
-Inject grout following similar concept to that for PU injection
-Continue to inject until grout is seen to emerge from neighbouring holes
-Repeat the process for other areas
Tile Grout Leakage – Impregnation
Tile grout leaking e.g. bathroom floor
-Grout seal to penetrate into tile joints and tile surface to provide water resistant properties
-3 layers of application by brush, roller, or spray
-Ensure dry condition during application and at least 3 hours after application
Re-tiling
Patching on the affected localised spots should suffice. If the surface is badly affected, re-levelling and re-tiling may be the most suitable remedy.
The screed is the crucial part before the tiling in order to achieve the desired gradient. A screed can be defined as a layer of well-compacted material applied in-situ to a structural base or other substrate and finished to a designated level.
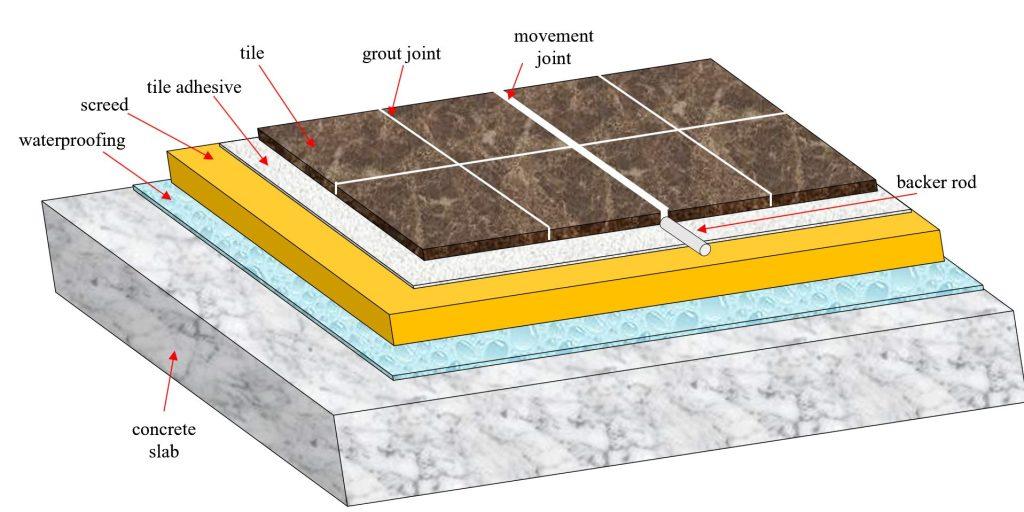
It serves:
– as a smooth, flat surface to a correct level for bedding of tiles
– as a protection for the waterproofing coating
– to provide falls to drain water off
– to accommodate service pipes

