Case 5
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Carry out surface cleaning and repair applications. Use a stiff brush to loosen joint grout and reinstate
joints with suitable tile grout. Remove and re-tile the affected areas in accordance with SS 637 or
equivalent (there may be a colour mismatch if stocks of extra tiles are unavailable). For areas where the wear is negligible, a mixture of cement and water slurry with a hardener may be painted over them. However, for large worn surfaces, it is necessary to hack off the screed and patch up with a suitable
mix of cement and sand screed together with a hardener in accordance with BS 8221-2 or equivalent.
Perform regular mopping/buffing of tiled surfaces. Proper handling of equipment to prevent damages
to the tile surface.
- Regular cleaning of tile is required to prevent any staining over the surface. Regular mopping and buffing is the main cleaning method. The thorough cleaning action should brighten the tile and joints.
- Use a solution of 1/4 cup low-sudsing detergent, or 1-2 tablespoons of either washing soda or trisodium phosphate or commercial floor cleaning powder in 1 gallon water to scrub with an electric floor washer or polisher-scrubber.
- Glazed tiles should be treated like porcelain enamels, because they are easily scratched if incorrect cleaning method is used.
- Avoid using harsh abrasive powders which will scratch the finish. Use plain water to remove soil.
- Occasionally for heavier soils, use a mild detergent solution, rinse well, and wipe dry for more shine.
- Special cleaning may be needed for ceramic tile if there is a buildup of: soap scum, a rough white coating, or mildew.
- In addition, regular inspections should be carried out periodically at regular intervals to detect the defects. This can begin with visual inspection and assessment process because it facilitates selection of other subsequent testing methods.
- Instruments can be used extensively to diagnose these defects properly and to take remedial action to keep the structure in good condition.
- Following instruments and techniques can be used to detect cracks in building elements.
Diagnostics of Defect (see also NDT)
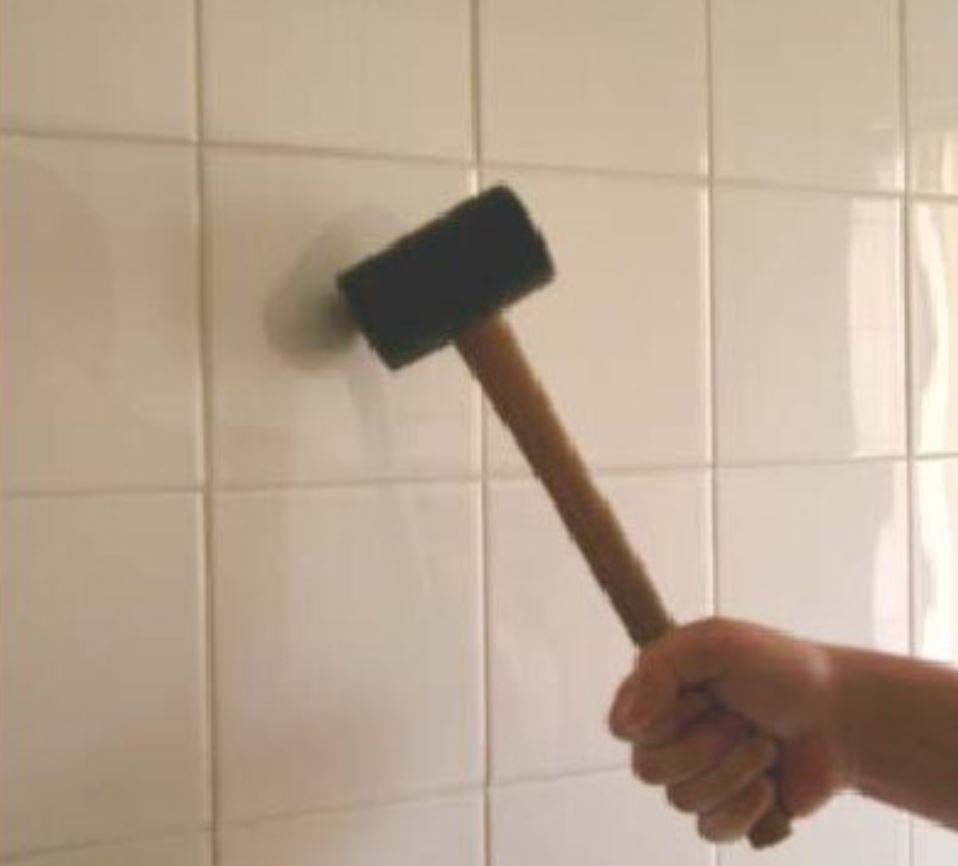
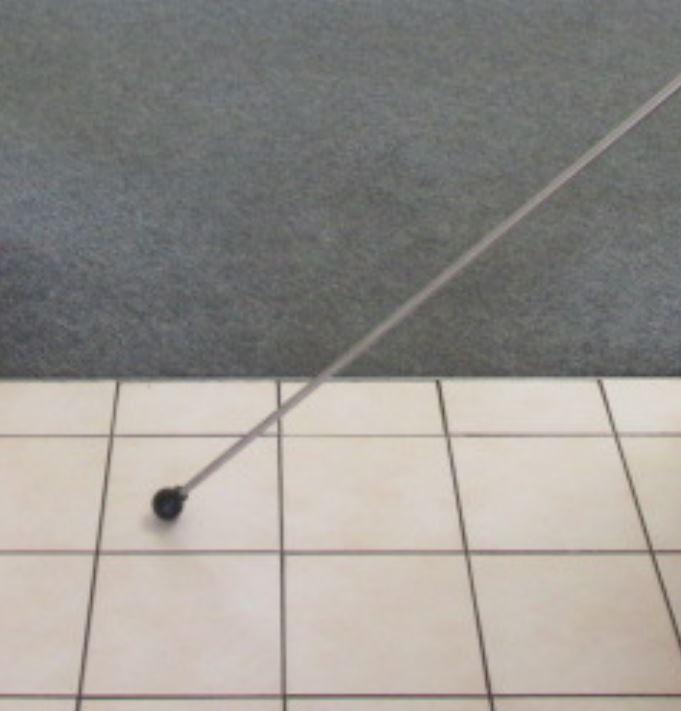
Hammer Tapping Test
Tapping test may be used to detect hollowness, delamination, spalled or debonded plaster.by listening to the ‘void’ sound.



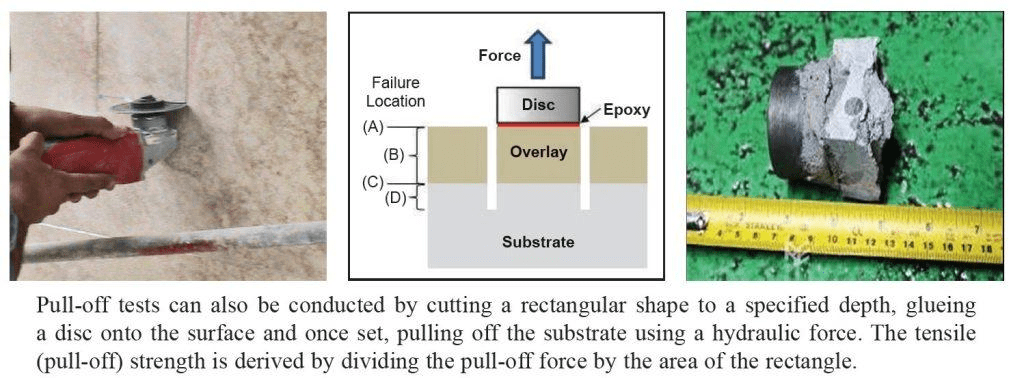
Pull-Out (Pull-Off) Test
The principle is to glue a dolly or plate onto the substrate and, once set, pull it out at a specified uniform increase in force until the dolly/plate is completely pulled off from the substrate. Observations are made on the pull-off stress, as well as the failure mode at the interface. The pull-off stress (MPa) is calculated by dividing the pull-off force (kN) by the area of the dolly/plate (mm2).