Hydrophobic Coating
Location of Façade Coatings in Singapore
Introduction
Self-cleaning materials are two-fold; i.e. super-hydrophobic or super-hydrophilic [4]. The lotus effect of the super-hydrophobic materials is achieved by transforming the microstructure of materials such as tiles or façade paint products. Super-hydrophilic surface on the other hand are realized by use of coating Titanium Dioxide (TiO2) on glass, tiles, or concrete surfaces.
One method for self-cleaning facades is to have a super-hydrophobic surface, this can be achieved by applying a super-hydrophobic paint or coating [6]. To be classified as a super-hydrophobic surface the contact angle between a droplet of liquid and the material, must be greater than 150 degrees compared to a hydrophobic surface were the contact angle must be greater than 90 degrees, as shown on Figure below.
![]()
Water behaviour in (left) typical and (right) hydrophobic surfaces
Discovered in the 1990s, this effect is also known as the Lotus-effect and have since been used to produce self-cleaning coatings [7]. It’s named after the lotus leaves ability to stay clean even in dirty conditions, and it is achieved by applying roughness on the surface on a nanometre and micrometre level. These nano- and micrometric structures reduces the capillary forces between the water droplet and the surface. As a result, water on such surfaces have contact angles higher than 130 degrees [4]. The water droplet takes almost a spherical form and can roll of easy, along with the particles of contaminants adhered to the droplet surface and hence are removed from the rough surface when the droplets roll off.
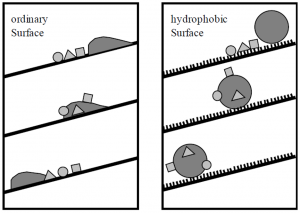
Demonstration of lotus effect on a hydrophobic surface (right) vs the ordinary surface (left) [4]
Particles on this kind of surface has a very little contact area with the material underneath and the bonding forces (adhesion forces) are reduced significantly. Once a droplet appears, the particles bond to the droplets instead and can be carried away.
These super-hydrophobic self-cleaning technologies and products are being used in more and more commercial products due to its aesthetic, economic and environmental benefits [8]. As the author confers, super-hydrophobic materials when applied to external surfaces reduces maintenance costs due to lesser labour and chemicals required for cleaning exercises at a lower environmental impact.
Hydrophilic surfaces on the other hand attract water droplets to the surface, where they will completely spread out and have a contact angle less than 5° (Figure 2.6). This can be applied or different kind of usages such as fast-drying surfaces, antifogging and evaporative cooling. Most interesting for façades are the anti-fogging and fast-drying application. Furthermore, these coatings have a high transparency which makes them highly interesting for application.

Water behaviour in hydrophilic surfaces
To attain these properties a surface needs to comprise both high surface energy and a high effective area. This is achieved by having a high roughness on the micro/nano scale, in the same way as the hydrophobic surfaces.
Recent advancements of the field introduced new methods of creating self-cleaning surfaces introducing roughness to TiO2 particles by photo-electrochemical etching [9]. This has enabled to create both hydrophobic and hydrophilic properties in the same surfaces [10]. This has expanded the application of TiO2 in self-cleaning products adding on to its already favourable benefits such as high catalytic efficiency, chemical stability, low toxicity, low cost, and good comparability with construction material [5].
For preparing a super-hydrophilic surfaces can be done based on etching, hydrothermal treatment, nanocomposite coatings, polymerization and layer-by-layer (LbL) [11]. The LbL principle is conducted by assembling the oppositely charge hydrophilic particle, which is most often done with silicon dioxide (SiO2) or titanium dioxide (TiO2) particles. This also resembles the procedure to create a hydrophobic surface.
Benefits of Façade Coatings
Hydrophobic paints are already available commercially in several European countries to safeguard buildings from the effect of weather and improve its appearance as it prevents corrosion, growth of mould in damp and cold areas, as well as water seepage and mildew.
Water repellent
Hydrophobic surfaces have excellent water repellent properties, which is due to a combination of surface roughness on either the micro or nanoscale level [12]. As there is insufficient energy to deform the fluid boundary to bring it in contact with the entire super-hydrophobic surface, the direct contact area between the surface and the fluid is limited to only the protruding nano-parts of the hydrophobic facade. Therefore, water will not be able to adhere to the surface well and will just roll off in a spherical shape in a phenomena known as beading [13]. This will help to keep the facade dry and free from any particles clinging to the wall, and therefore there is minimal chance for biological growth on the surface of the wall, thus making the durability of the facade longer.
Hydrophobic surfaces allows air and water vapour to permeate through due to its porous structure [14]. This will help to lower the thermal conductivity of the wall and hence it encourages thermal insulation as air is able to permeate through the paint.
As air and water vapour does not trap in between the hydrophobic paint and the facade, there will be less likely to have pressure built-up due to the expansion of trapped air on a hot day and hence blistering of the facade will less likely to occur [15].
Most conventional hydrophobic surfaces will lose their hydrophobic characteristics when exposed to prolong ultraviolet rays (UV) [16]. However, hydrophobic surfaces that are made of silica using the sol-gel processing method are shown to retain its hydrophobic properties after 5,500 h of ultraviolet (UV) irradiation without degradation of either contact angle or contact angle hysteresis [17].
Resistant to biological agents
Having hydrophobic coatings are known to reduce biofouling of underwater structures and ships’ hulls in underwater by forming a hydrophobic rough surface that supports an air film between itself and the water [18]. The reduction of the wetted area reduces the ability for biological organisms to adhere encounter on the underwear structures. Research have done that as compared to normal substrates, almost no micro-organisms attached to the super hydrophobic surfaces in the first week after immersion [19].
Corrosion and Pollutant Resistant
Given their excellent water repellence properties, hydrophobic coatings are known to slow down the breaking of the oxide layer of metals caused by water and thus prevent the metal or alloy surface underneath from further corrosion [20].
Reduction of cleaning resources
Given the fact that rainwater is only required to clean the facade coated with hydrophobic coating and remove the air pollutants on the facade surface, it can be inferred that potential savings can be realised in terms of reduction of maintenance required (water, electricity and human resources) in cleaning the facade, unless there is a prolong period of drought.