Case 1
Navigation
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Remedial (see also Remedial)



- Replacing the cracked brick units along the length of the crack and grinding and pointing cracked mortar joints full depth.
- Cracks and gaps can be patched with weather resistant filler which contain a resin/ binder system.
- Pressure grouting with structural adhesives
- Before work is performed, determine that no large voids or cavities exist inside the wall
- apply a temporary seal to the crack,
- injection ports are inserted at regular intervals,
- inject adhesive into the ports. The adhesive used is often a clear, two-component, compatible epoxy resin compound.
- Sealing the cracks with a good quality sealant can be an effective repair (Figure 1a, b & c).
- Prior to installing sealant, grind the cracks to a width of approximately 1/4 to 3/8 inch and a depth of roughly twice the width. Install a backer rod to create a good joint profile and to avoid creating a sealant joint that is bonded along three sides.
- Sealant joints bonded along three sides are prone to failure when there is any movement across the crack. In many cases, it may be necessary to prime the masonry.
- In some cases, the appearance of these sealant joints can be improved by applying sand onto the surface of the uncured sealant.
- This procedure may have some impact on the movement capability of the sealant joint; however, if appropriate repairs are implemented to address the cause of the cracking, significant movement across the crack should not occur.
- Where significant movement is expected, the sealant manufacturer should be contacted to evaluate the suitability of this approach.
- If the crack is not wider than 3mm, repaint the surface to conceal the crack (Figure 2).

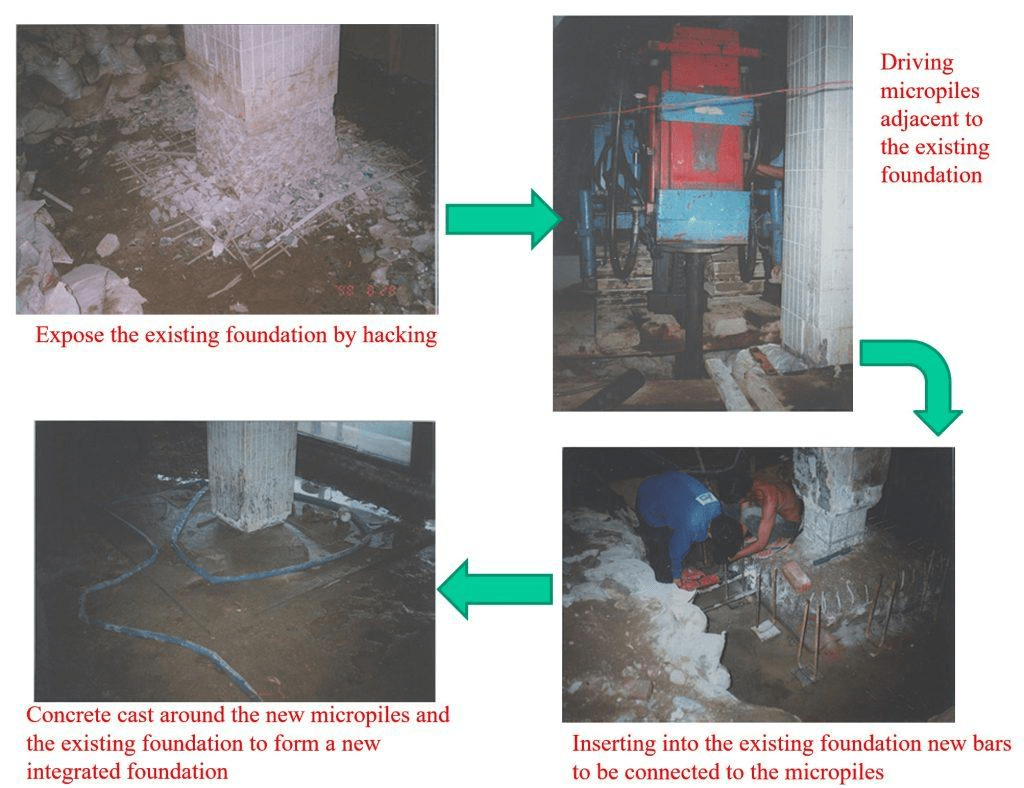
In the case of structural cracks due to movements, a cosmetic repair (filling and patching) does not work. The cause for the structural crack must first be evaluated before the most optimum repair method can be determined. This may involve stabilising the foundations such as underpinning, strengthening weakened elements such as reinforcing the structure with additional steel or other materials etc.
Underpinning