Case 3
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
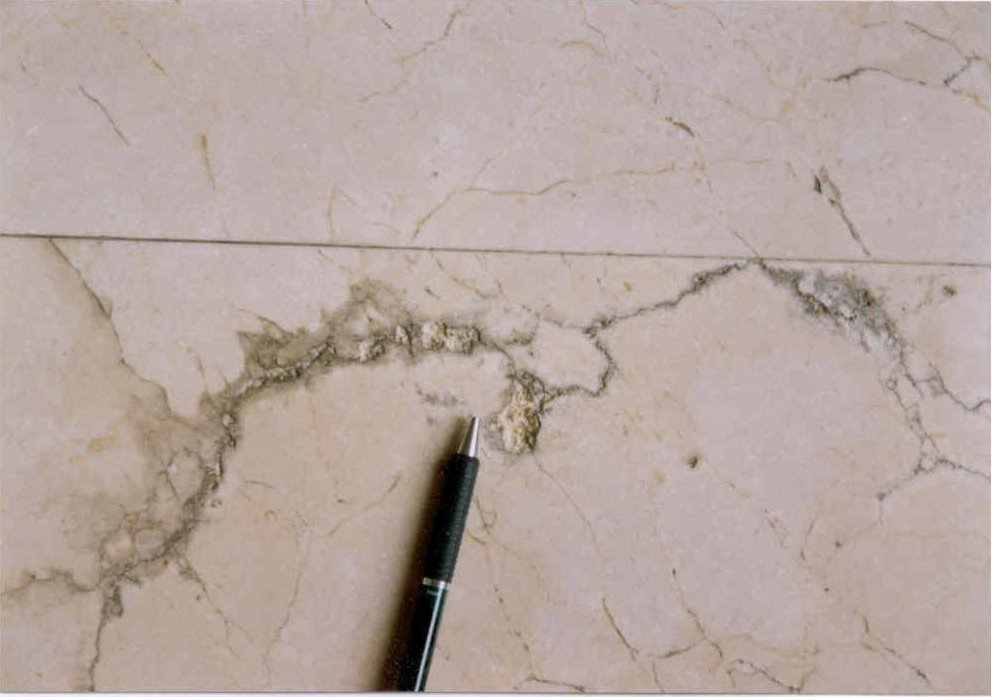
Staining along Veins

Introduction
Building Type: Commercial
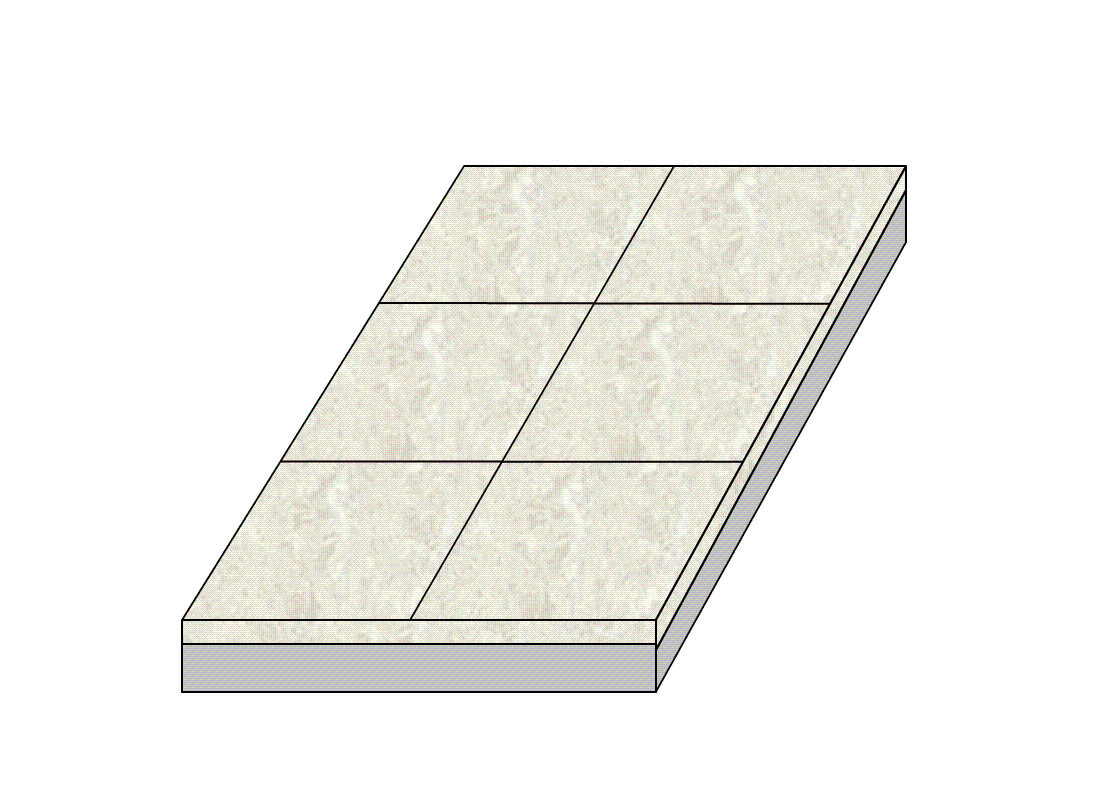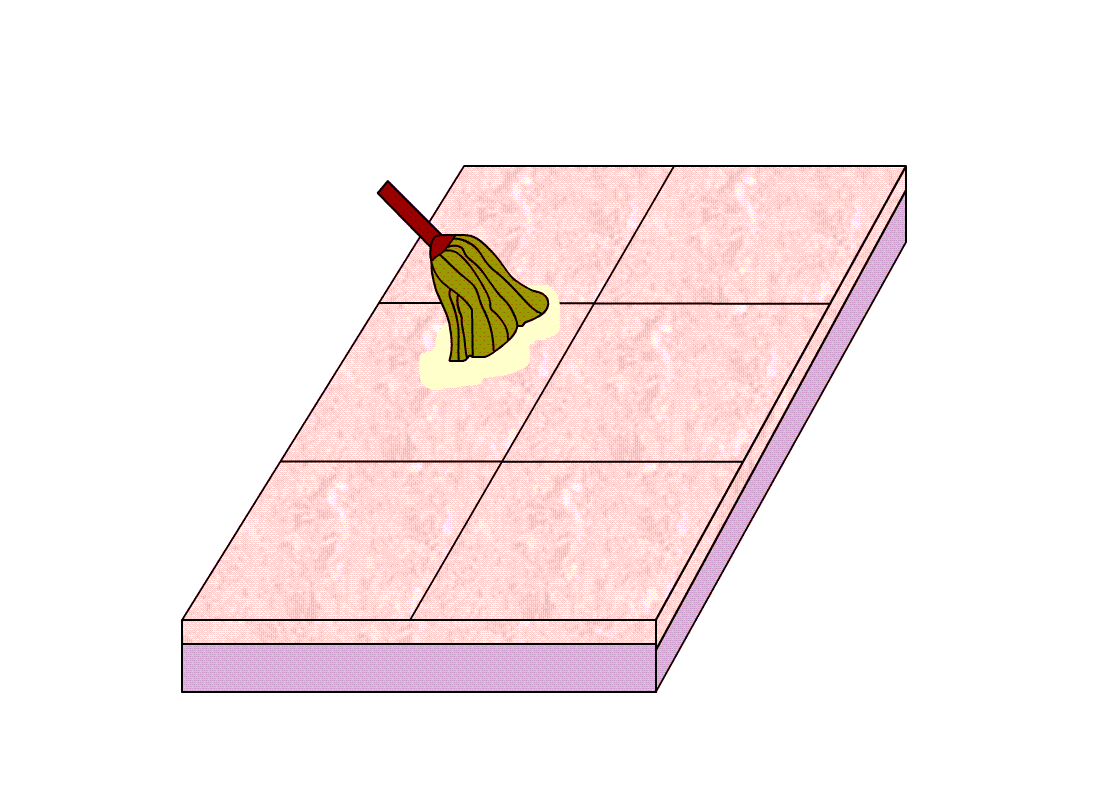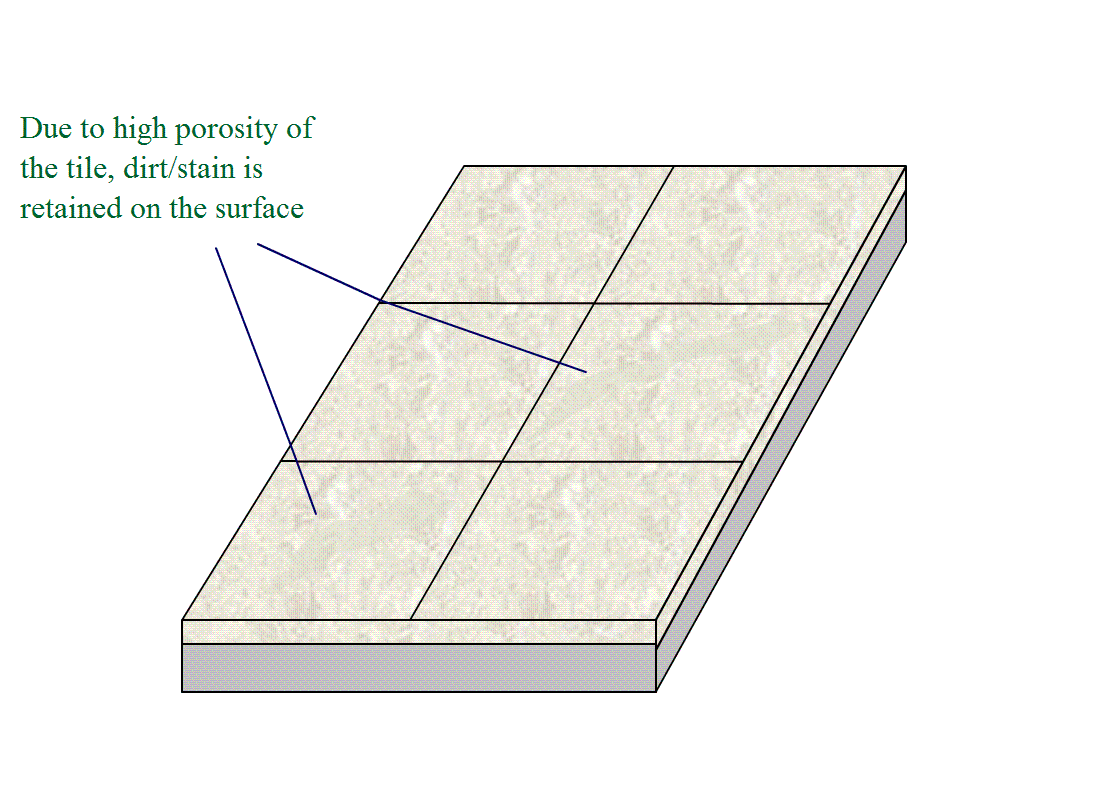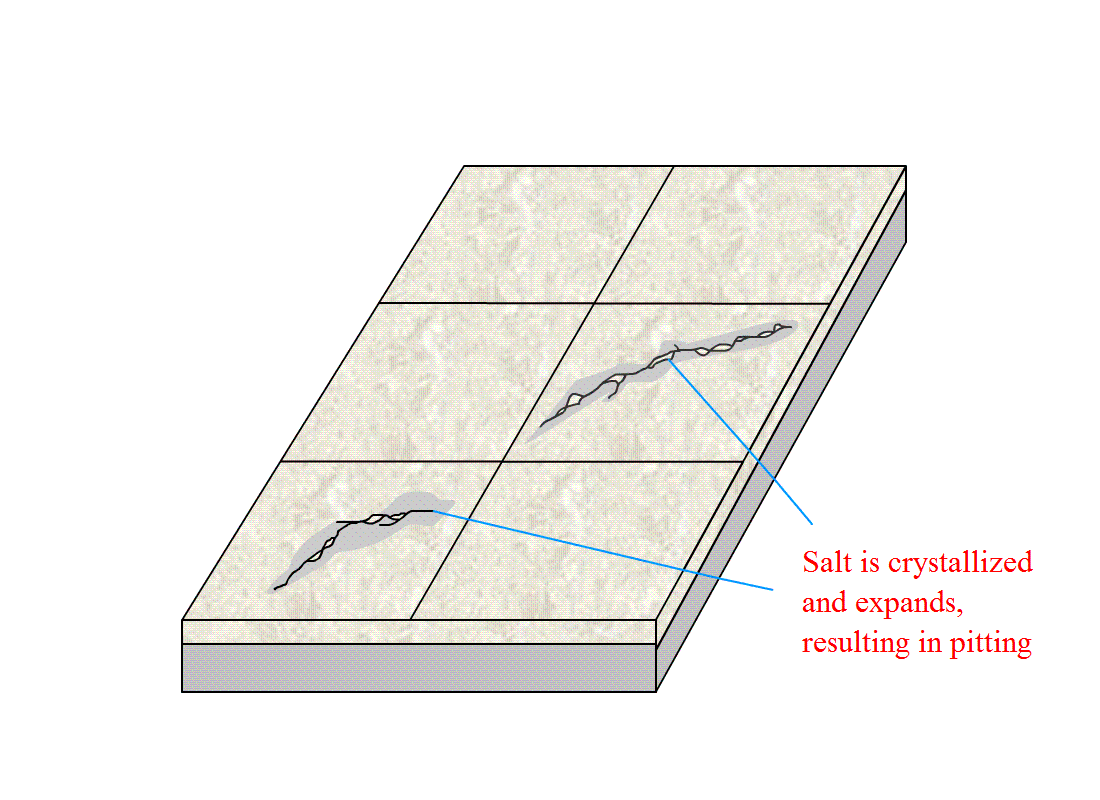
In this case, a marble floor in a commercial building is pit and stained along its natural vein as shown. Crack and flaking of the surface along some of these natural veins and loss of gloss on areas with dark patches were observed. Stain was mainly caused by salt in which Sodium (Na), Potassium (K), Iron (Fe) and Sulfur (S) content appeared high. There are also cases where minerals from the natural stones migrate to the surface to form stains of various colours.
Being a natural stone, marble may be porous depending on the nature of constituents and the formation process. This porosity may allow marble tiles to retain dirt/stains under circumstances.
Salt from the bedding and/or grout or mineral may be brought onto the surface of the marble through micro pores or cracks onto the surface under wet conditions. Some salts are hygroscopic and tend to absorb moisture from the humid environment or physical water which is presents in the wet area floor. Upon drying, the salt will crystallize and expand resulting in pitting.


