Case 3
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Maintenance and Diagnostics
Maintenance
Remove source of staining in accordance with BS 8221-1, SS 509-1 or equivalent. Mop and buff commercial areas thrice a day and other areas twice a day. Fortnightly, machine scrub floors to remove
grout stain. Perform monthly hand scrubbing of walls. Use commercial tile cleaner to remove efflorescence twice a year. Use diluted chlorine bleach/mildew-retardant spray for mildew, and in areas of
deep soiling and hard to reach areas. Biological growth can be removed by scrubbing with an acid/alkali based cleaner. Biocidal washes may be applied to prevent further growth. Remove severe soiling by scrubbing with acid/alkali based cleaner. Check for pointing defects and other anomalies including chipping, crazing, cracking and adhesion/cohesion failure on the joints. Ensure efficient drainage and ventilation to have the wet area remain in a dry condition as much as possible. Check tile condition for chipping, cracks and hollowness.
- Regular cleaning of marbled surface is needed to remove dirt.
- Regular cleaning can be done with any cleaning solution which contains any form of acids, phosphorus, chlorine or scouring powders should not be used on polished marble, since this would make marble looks dull or suffer from a peeling effect known as “orange peel” unless adhering to the cautions and/or formulas provided. In addition, any type of abrasive product should also be avoided, in order to prevent scratches and loss of shine.
- For polished finishing small areas, use of warm water would be sufficient for periodic cleaning
- Use a solution of 1/4-cup low-sudsing detergent, or 1-2 tablespoons of either washing soda or trisodium phosphate or commercial floor cleaning powder in 1 gallon of water to scrub with an electric floor washer or polisher-scrubber.
- Glazed tiles should be treated like porcelain enamels, because they are easily scratched if incorrect cleaning method is used.
- Avoid using harsh abrasive powders, which will scratch the finish. Use plain water to remove soil.
- Occasionally for heavier soils, use a mild detergent solution, rinse well, and wipe dry for more shine.
- Special cleaning may be needed for ceramic tile if there is a buildup of: soap scum, a rough white coating, or mildew.
- In addition, regular inspections should be carried out periodically at regular intervals to detect the defects. This can be begun with visual inspection and assessment process because it facilitates selection of other subsequent testing methods.
- Instruments can be used extensively to diagnose these defects properly and to take remedial action to keep the structure in good condition.
Diagnostics of Defects (see also NDT)
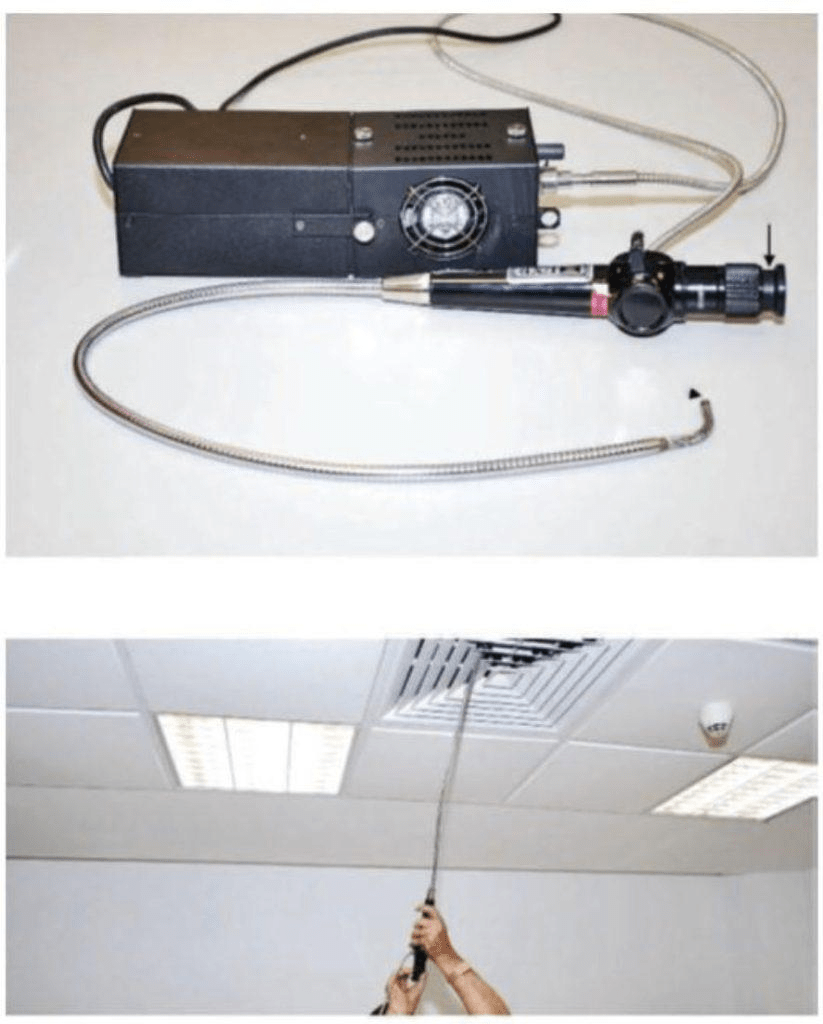
This instrument is useful when services are concealed. There have been many cases of collapse of large area of false ceiling, due to weight of accumulation of water or condensate. Regular inspection using a fibrescope/borescope could prevent such accidents.
A fibrescope or a flexible borescope is a flexible optical inspection device that consists of fibre optic bundles with an eyepiece at one end and a lens at the other.
A fibrescope usually comes in two bundles: (i) a fibre optic light bundle that is for illuminating the object to be investigated, and (ii) a fibre optic image bundle to relay the image to the eyepiece. It allows a direct visual inspection for an otherwise inaccessible part, as observations of remote, difficult-to-reach areas can be made through a video monitor with high-resolution images. The flexible fibres allow it to be manoevred in hard-to-reach or inaccessible areas.
It is often used to verify findings from other tests, such as infrared thermography or impact-echo testing.
Common applications include:
– Inspection of connecting condition behind the external cladding wall of a building.
– Inspection of defects on concrete surface(s) in a deep and narrow gap.
– Determination of corrosion condition of steel tendon(s) inside post-tensioning ducts of pre-stressed structural member(s).
– Investigation of service pipes, ducts and other inaccessible areas.
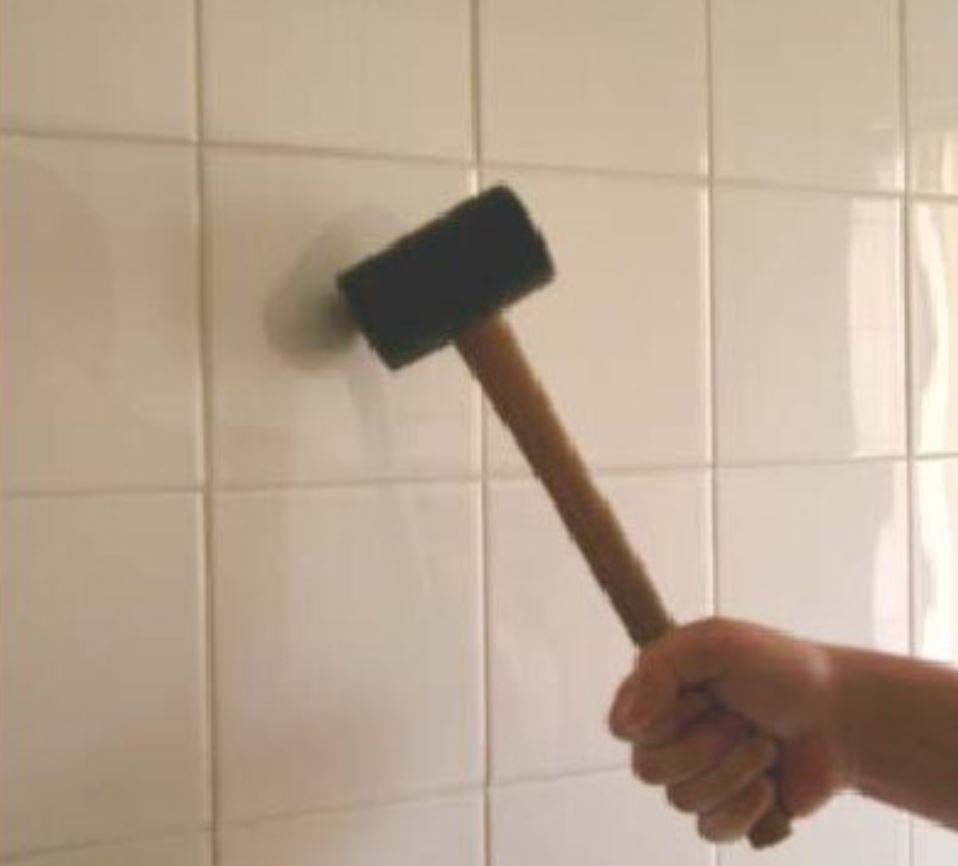
Hammer Tapping Test
Tapping test may be used to detect hollowness, delamination, spalled or debonded plaster.by listening to the ‘void’ sound.
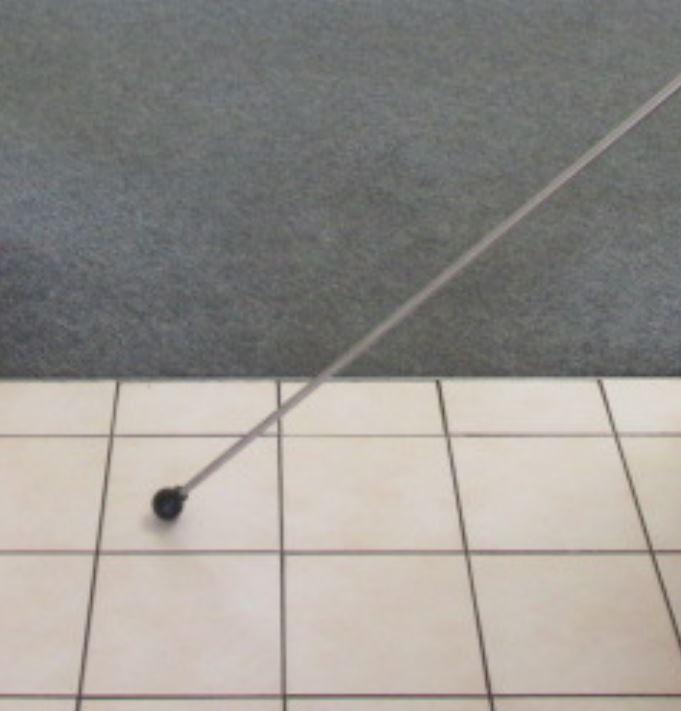




Protimeter / Moisture Meter
Moisture meter is used to determine the presence of moisture. Moisture readings can be taken within masonry walls, dry walls, insulation, concrete members, roofing, wood construction, and other building components.
