Case 4
- Introduction
- Causes of Defects
- Good Practices
- Standards
- Maintenance and Diagnostics
- Remedial
- Similar Cases
- References
Remedial (see also Remedial)
Where the cracks penetrate not only the plastering but also the background, the cause of the cracking should be ascertained and dealt with before proceeding with the repair. The background should be first made good. Where it is not possible to effect complete repair of the background, the plastering should be cut back on both sides of the crack for at least 150mm and light expanded metal over building material or polyethylene sheet should be fixed to the background and embedded in the undercoat of the plastering.
The patches of damaged plastering should be cut out preferably in rectangular areas, down to the background. The exposed edges of the plastering should be slightly undercut. The exposed surface of the background should be well brushed to remove dirt or loose material and should be washed.
The area cut out should be made good according to the nature of the background and the type of finish as stated in the BS.
Bonding agents are particularly useful when carrying out minor patching work.
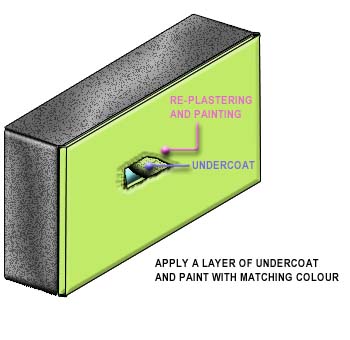
The colour and texture of the new plastering should be matched as closely as possible to the existing work.
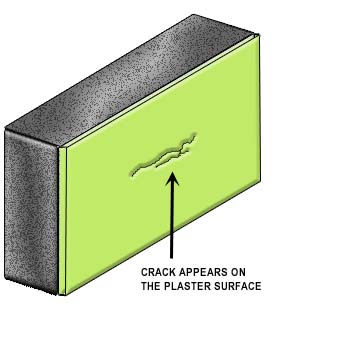
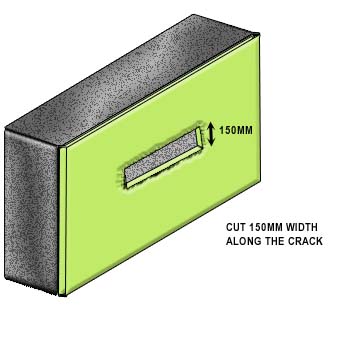

Where the cracks penetrate not only the plastering but also the background, the cause of the cracking should be ascertained and dealt with before proceeding with the repair. The backing wall should be first made good. Where it is not possible to effect complete repair of the background, the plastering should be cut back on both sides of the crack for at least 150mm and light expanded metal over building material or polyethylene sheet should be fixed to the background and embedded in the undercoat of the plastering (Figure 1a to 1d).


- The patches of damaged plastering should be cut out preferably in rectangular areas, down to the background. The exposed edges of the plastering should be slightly undercut (Figure 2a).
- The exposed surface of the backing wall should be well brushed to remove dirt or loose material and should be washed.
- The area cut out should be made good according to the nature of the background and the type of finish as stated in the BS.
- Bonding agents are particularly useful when carrying out minor patching work.
- The colour and texture of the new plastering should be matched as closely as possible to the existing work.
An example of heritage conservation work involving Shanghai plaster restoration is shown below: